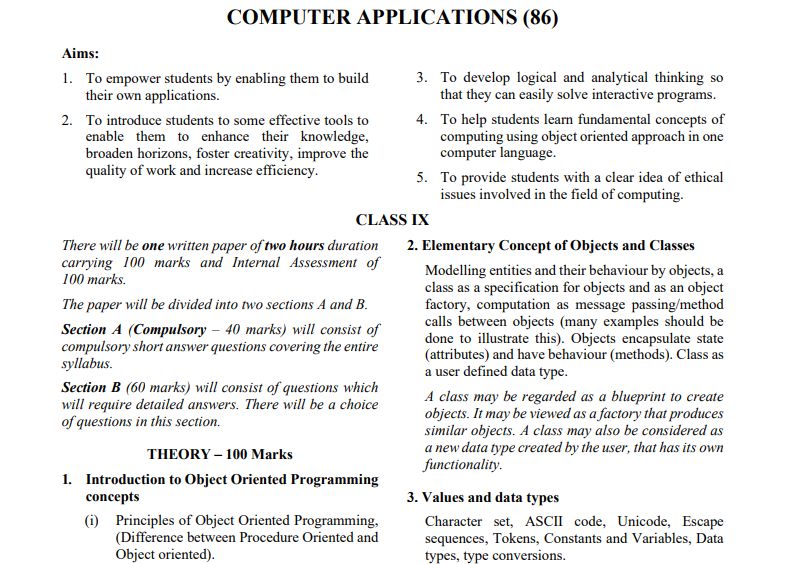
The ICSE Class 10 Computer Applications syllabus includes a theory paper (100 marks) and internal assessment (100 marks) with practical assignments. The theory covers revision of Class IX topics like basic Java, object-oriented concepts, data types, operators, conditionals and loops. It then advances to classes and objects, user-defined methods, constructors, library and wrapper classes, encapsulation, arrays (single and double dimensional) and string handling. Practical work emphasizes programming skills with a minimum of 20 lab assignments to reinforce concepts studied in theory. The course tests both programming and conceptual understanding.
ICSE Class 10 Computer Application Syllabus 2026
The ICSE Class 10 Computer Application Syllabus for 2025-26 provides students with a structured framework to understand core computing concepts and programming skills using Java. It covers essential topics, such as Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) principles, data types, methods, constructors, arrays, string handling, and encapsulation. This syllabus is designed to ensure students build a solid foundation in programming and problem-solving, preparing them for more advanced computer science studies.
ICSE Class 10 Computer Application Syllabus 2025-26: Details
Assessment Structure:
| Assessment Type | Marks | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Written Paper | 100 | 2 hours |
| Internal Assessment | 100 | Practical-based |
Written Paper Structure
- Section A (40 Marks): Compulsory short answer questions on the full syllabus.
- Section B (60 Marks): Detailed questions with choices for in-depth responses.
ICSE Class 10 Computer Application Syllabus 2026: Topics wise
- Class IX Revision Topics
- Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
- Objects and Classes
- Data Types and Values
- Operators and Input in Java
- Conditional and Iterative Constructs
- Nested Loops
- Class as Basis of Computation
- Objects and Classes: Representing state and behavior
- Variable Types: Primitive vs. composite data types
- Real-life Examples of Classes and Objects
- User-Defined Methods
- Method Definition, Syntax, and Overloading
- Invocation Methods: Call by Value and Call by Reference
- Static vs. Non-static Methods, Modular Programming
- Polymorphism through Method Overloading
- Constructors
- Constructor Characteristics and Types
- Difference Between Constructor and Method
- Constructor Overloading and Usage
- Library Classes
- Introduction to Wrapper Classes
- Autoboxing and Unboxing
- Common Wrapper Class Methods (e.g., parseInt, isDigit, isLetter)
- Encapsulation
- Access Specifiers: Private, Protected, Public
- Scope and Visibility of Variables
- Arrays
- Single and Double Dimensional Arrays
- Sorting (Selection and Bubble Sort) and Searching (Linear and Binary Search)
- Matrix Display and Operations (Sum of Rows, Columns)
- String Handling
- String Class Methods (e.g., trim, concat, substring, indexOf)
- Programs on String Manipulation, Sorting, and Searching
Internal Assessment (100 Marks)
The practical-oriented segment focuses on enhancing programming skills. Students are expected to complete a minimum of 20 laboratory assignments to reinforce class concepts.
Sample Assignment Topics
| Topic | Examples |
|---|---|
| User-defined Methods | Programs on pure/impure, static/non-static methods |
| Constructors | Programs on constructor types and overloading |
| Library Classes | Programs on wrapper class methods and character checks |
| Encapsulation | Identifying variable types and access specifiers |
| Arrays | Programs on array operations, sorting, and searching |
| String Handling | String manipulation, palindrome check, and alphabetical order |
Practical Evaluation Criteria
| Criteria | Excellent | Good | Fair | Poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class Design | 10 | 8 | 6 | 4 |
| Variable Description | 10 | 8 | 6 | 4 |
| Coding and Documentation | 10 | 8 | 6 | 4 |
| Execution/Output | 20 | 16 | 12 | 8 |
Equipment and Software Requirements
| Recommended Equipment | Description |
|---|---|
| Lecture Room | Multimedia Projector or LCD and Whiteboard |
| Computer Lab | One computer per student, minimum 1 GB RAM, P-IV CPU |
| Peripherals | Quality printers, scanner, and optional webcam |
| Software | Blue J or compatible IDE with JDK version 5.0+ |
ICSE Class 10 Computer Application Syllabus 2025-26 PDF Download
Students and educators can download the ICSE Class 10 Computer Application Syllabus PDF for 2025-26 to get a comprehensive view of the syllabus, assessment methods, and practical requirements. The PDF serves as a quick reference guide to understand exam patterns, key topics, and evaluation criteria.
ICSE Class 10 Computer Application Syllabus-Click Here To Download PDF
FAQs Based on ICSE Class 10 Computer Syllabus
1. What is the subject name for ICSE Class 10 Computer?
The subject is officially called Computer Applications under the ICSE (CISCE) curriculum.
2. Which programming language is prescribed in ICSE Class 10 Computer?
ICSE Class 10 Computer Applications uses Java as the programming language.
3. What is the exam pattern for ICSE Class 10 Computer Applications?
The exam consists of two papers:
-
Paper 1 (Theory) – 100 marks
-
Paper 2 (Practical) – 100 marks
Both papers are compulsory for final evaluation.
4. What are the major topics in ICSE Class 10 Computer Theory syllabus?
Key theory topics include:
-
Objects and Classes
-
Data Types, Variables, and Operators
-
Conditional Statements (if, switch)
-
Looping Statements (for, while, do-while)
-
Arrays (1D & 2D)
-
String Handling
-
User-defined Methods
-
Library Classes (Math, String)
5. Is object-oriented programming important for the ICSE exam?
Yes, Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a core part of the syllabus, focusing on classes, objects, constructors, and methods.
6. What is covered in the ICSE Class 10 Computer Practical exam?
The practical exam includes:
-
Writing Java programs
-
Program logic and output
-
Project work
-
Practical file submission
-
Viva voce
7. How many programs are asked in the practical exam?
Students are generally required to solve two Java programs, testing logic, syntax, and problem-solving skills.
8. Are arrays and strings important for ICSE Class 10 Computer?
Yes, arrays and strings are among the most frequently asked topics in both theory and practical exams.
9. What type of questions are asked in the theory paper?
The theory paper includes:
-
Short answer questions
-
Program-based questions
-
Output prediction
-
Conceptual explanations
-
Structured questions
10. Is project work compulsory in ICSE Class 10 Computer?
Yes, project work is mandatory and carries marks as part of the practical assessment.
11. How can students score well in ICSE Class 10 Computer Applications?
Students should:
-
Practice Java programs regularly
-
Understand program logic instead of memorizing
-
Revise theory definitions and syntax
-
Solve previous years’ question papers
12. Are library classes important for the exam?
Yes, questions based on Java library classes like Math and String are commonly asked.
13. Is the ICSE Class 10 Computer syllabus difficult?
The syllabus is concept-based, not difficult if students practice coding consistently and understand fundamentals.
14. Are previous year papers useful for preparation?
Absolutely. Solving previous year question papers helps understand exam pattern, marking scheme, and important topics.
15. What is the best way to prepare for output-based questions?
Practice writing and tracing Java programs step-by-step to understand flow of execution and variable changes.
About The Author
Brajesh
Brajesh (MCA, M.Tech (IT)) is a passionate education and career content creator with a strong academic background in Computer Applications (MCA) and Technology (M.Tech). With years of hands-on experience in exam preparation strategies, syllabus analysis, and government job updates, he helps students and aspirants navigate their academic and professional journeys with clarity and confidence.