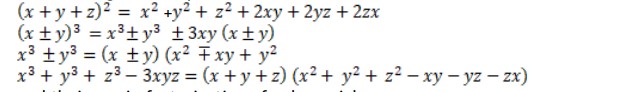In the Class 9 Curriculum, Mathematics is one of the most crucial subjects among all. To do well in the maths exam, you need to master all the concepts mentioned in the official CBSE Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2025-26.
Understanding the CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Syllabus 2025-26 enables students to create academic goals and arrange their studies properly in order to accomplish them. Read the full blog to know about the CBSE Class 9 Maths Topics, Marks distribution and so on.
CBSE Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2025-26
Mathematics is such a subject that matters for grades for students in Class 9 Standard. To achieve high scores in the Class 9 Maths exam, you need to grasp the concepts efficiently and then practice them again and again.
As per the CBSE Class 9 Syllabus of Maths, there are a total of 6 units, namely- Number System, Algebra, Coordinate Geometry, Geometry, Mensuration, and Statistics. Students are recommended to go through the whole syllabus to familiarize themselves with the concepts and topics included in it.
Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2025-26 Marks Distribution
For the current academic year, the CBSE Class 9 Maths syllabus is essentially the same as it was last year. Notably, there are also no notable changes to the examination pattern. The total marks allotted for the Class 9 Maths Exam is 100 Marks, which is divided into two:
- Theory/Written Exam: 80 Marks
- INTERNAL ASSESSMENT- 20 Marks
Let’s take a quick tour of the unit-wise marks distribution of the CBSE Class 9 Maths Syllabus in the table below.
| S. No. | Name of Unit | Marks |
| 1 | NUMBER SYSTEMS | 10 |
| 2 | ALGEBRA | 20 |
| 3 | COORDINATE GEOMETRY | 4 |
| 4 | GEOMETRY | 27 |
| 5 | MENSURATION | 13 |
| 6 | STATISTICS & PROBABILITY | 6 |
| TOTAL | 80 |
CBSE Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2025-26 Unit Wise
The Class 9 Mathematics Syllabus is divided into six units, and each unit discusses a unique concept of the Mathematical Operations. Here we have shared a list of topics and subtopics included in the CBSE Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2026.
UNIT I: NUMBER SYSTEMS
| UNIT I: NUMBER SYSTEMS | |
| 1. REAL NUMBERS |
|
UNIT II: ALGEBRA
| Unit II: ALGEBRA | |
| 1. POLYNOMIALS |
|
| 2. LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES | Recall of linear equations in one variable. Introduction to the equation in two variables. Focus on linear equations of the type ax + by + c=0.Explain that a linear equation in two variables has infinitely many solutions and justify their being written as ordered pairs of real numbers, plotting them and showing that they lie on a line. |
UNIT III: COORDINATE GEOMETRY
| UNIT III: COORDINATE GEOMETRY | |
| COORDINATE GEOMETRY | The Cartesian plane, coordinates of a point, names and terms associated with the coordinate plane, notations. |
UNIT IV: GEOMETRY
| UNIT IV: GEOMETRY | |
| 1. INTRODUCTION TO EUCLID’S GEOMETRY | History – Geometry in India and Euclid’s geometry. Euclid’s method of formalizing observed phenomenon into rigorous Mathematics with definitions, common/obvious notions, axioms/postulates and theorems. The five postulates of Euclid. Showing the relationship between axiom and theorem, for example:
|
| 2. LINES AND ANGLES |
|
| 3.TRIANGLES |
|
| 4. QUADRILATERALS |
|
| 5. CIRCLES |
|
UNIT V: MENSURATION
| UNIT V: MENSURATION | |
| 1. AREAS | Area of a triangle using Heron’s formula (without proof) |
| 2. SURFACE AREAS AND VOLUMES | Surface areas and volumes of spheres (including hemispheres) and right circular cones. |
UNIT VI: STATISTICS
| UNIT VI: STATISTICS | |
| STATISTICS | Bar graphs, histograms (with varying base lengths), and frequency polygons |
CBSE Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2025-26 PDF Download
The Central Board of Secondary Education has released an official CBSE Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2025-26 PDF on its official website at cbseacademic.nic.in. Apart from the syllabus, it contains crucial details like the marking scheme, exam pattern, unit-wise breakdown, and so on. To get more details, download the Class 9 Syllabus PDF by clicking the direct link given below.
CBSE Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2026: FAQs
1. What is the CBSE Class 9 Maths syllabus for 2026?
The Class 9 Mathematics syllabus follows the NCERT/CBSE curriculum and includes six major units:
-
Number Systems
-
Algebra
-
Coordinate Geometry
-
Geometry
-
Mensuration
-
Statistics
(Source: CBSE syllabus references & educational sites)
Each unit comprises important chapters and concepts students must learn for the annual exam.
2. How many units and marks are there in the syllabus?
The syllabus is divided into six units with the following theory marks distribution:
| Unit | Name | Marks |
|---|---|---|
| I | Number Systems | 10 |
| II | Algebra | 20 |
| III | Coordinate Geometry | 4 |
| IV | Geometry | 27 |
| V | Mensuration | 13 |
| VI | Statistics | 6 |
| Total (Theory) | — | 80 |
Internal assessment (not shown above) contributes 20 marks, making the overall evaluation out of 100.
3. What are the main topics under each unit?
Number Systems
• Real numbers and their decimal expansions (rational/irrational).
• Representation on the number line.
• Operations on real numbers.
Algebra
• Polynomials.
• Linear equations in two variables and their solutions.
Coordinate Geometry
• Cartesian plane and coordinates of points.
Geometry
• Euclid’s geometry fundamentals, lines & angles.
• Triangles and their congruence.
• Quadrilaterals and circles.
Mensuration
• Heron’s formula for the area of a triangle.
• Surface areas and volumes of 3D shapes.
Statistics
• Data representation and basic statistics.
4. Is the syllabus for 2026 different from previous years?
There hasn’t been a major reduction or structural change in the Class 9 syllabus for 2025-26 (which applies to the 2026 annual exams). The units and topics remain consistent with the latest official guidelines.
However, students should check for deleted topics (specific sub-topics removed from NCERT books), as indicated in rationalisation lists, to avoid studying content not evaluated in exams.
5. What is the exam pattern for Class 9 Maths 2026?
The main exam structure (80 marks) includes multiple types of questions:
-
∼20 MCQs (1 mark each)
-
Short answers (2–3 marks)
-
Long answers (5 marks)
-
Case-based questions (4 marks)
There is internal choice in some questions to help students answer according to comfort.
6. Do I need to study all chapters of NCERT?
Yes, NCERT Class 9 Maths textbook is the primary resource. Focus on conceptual understanding and all exercises, since the exam tests both fundamental and applied knowledge.
Also, check which topics have been deleted or rationalised in the curriculum so you don’t spend time on content not included in the current syllabus.
7. Which chapters are important or high-weightage?
Most units carry significant marks, but traditionally:
-
Algebra and Geometry have the highest weightage.
-
Understanding of Real Numbers, Triangles, and Surface Areas & Volumes is critical for exams.
8. Are there any changes planned in the assessment for Class 9?
CBSE has announced that open-book assessments (OBAs) for Class 9 will be introduced from the 2026-27 academic session (next year), promoting analytical and application-based learning.
This may influence future evaluation formats, but for the 2026 board exams, the traditional format applies.
9. Where can I download the official syllabus PDF?
You can download the official CBSE Class 9 Maths syllabus PDF from the CBSE Academic website under the “Curriculum 2025-26” section.
10. Quick tips for preparation
-
Start with the NCERT textbook and finish all exercises.
-
Practice sample papers based on the exam pattern.
-
Revision of core concepts regularly improves problem-solving speed.
-
Focus on diagrams and proofs in Geometry. (General guidance based on typical CBSE prep norms)