The GATE Civil Engineering (CE) Syllabus 2026 plays a crucial role for aspirants aiming to secure admission into top postgraduate programs or land prestigious PSU jobs. Designed by the exam authorities to evaluate a candidate’s mastery of core civil engineering concepts, the updated syllabus ensures a balanced mix of analytical ability, mathematical skills, and in-depth subject knowledge. GATE CE 2026 covers a wide range of topics, including Engineering Mathematics, Structural Engineering, Geotechnical Engineering, Environmental Engineering, Transportation Engineering, Water Resources Engineering, and Surveying. Each section is carefully structured to test both theoretical understanding and practical problem-solving skills relevant to modern engineering challenges.
With increasing competition every year, a clear understanding of the syllabus helps candidates plan their preparation strategically. GATE CE not only assesses technical expertise but also evaluates logical reasoning and application-based thinking through General Aptitude and core subject questions. The 2026 syllabus retains its comprehensive nature while aligning with evolving trends in civil engineering education and industry requirements. Aspirants are advised to thoroughly study each topic, refer to standard textbooks, and practice previous years’ papers to achieve a competitive edge. A well-planned approach, beginning with the syllabus breakdown, is the key to success in GATE Civil Engineering 2026.
GATE CE 2026: Syllabus Overview & Section-wise Layout
The GATE CE exam broadly has three parts:
| Section | Typical Weightage / Share |
|---|---|
| General Aptitude | ~ 15%. |
| Engineering Mathematics | ~ 13%. |
| Core Civil-Engineering Subjects | ~ 72–75% overall paper. |
The core civil-engineering domain further splits into several subfields like (but not limited to):
-
Structural Engineering (including Analysis & Design — RC/Steel)
-
Geotechnical Engineering (Soil Mechanics, Foundation, etc.)
-
Water Resources / Hydraulics / Hydrology / Fluid Mechanics
-
Environmental Engineering (Water/Wastewater, Air Pollution, Waste Management)
-
Transportation Engineering (Highways, Traffic, Pavement)
-
Geomatics / Surveying / Remote Sensing (less weightage compared to others)
-
Construction Materials & Management, Steel & RC Design, etc.
GATE General Aptitude Syllabus 2025
Quantitative Aptitude
Data interpretation: data graphs (bar graphs, pie charts, and other graphs representing the data), 2- and 3-dimensional plots, maps, and tables. Numerical computation and estimation: ratios, percentages, powers, exponents, and logarithms, permutations, and combinations, and series. Mensuration and geometry, Elementary statistics and probability.
Analytical Aptitude
Logic: deduction and induction, Analogy, Numerical relations, and reasoning
Verbal Aptitude
Basic English grammar: tenses, articles, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions, verb-noun agreement, and other parts of speech Basic vocabulary: words, idioms, and phrases in context Reading and comprehension Narrative sequencing
Spatial Aptitude
Transformation of shapes: translation, rotation, scaling, mirroring, assembling, and grouping Paper folding, cutting, and patterns in 2 and 3 dimensions.
GATE Structural Engineering Syllabus 2025
Engineering Mechanics
Internal forces in structures; Friction and its applications; Kinematics of point mass and rigid body; System of forces, free-body diagrams, equilibrium equations; Centre of mass; Euler’s equations of motion; Energy methods; Impulse Momentum; Principles of virtual work.
Solid Mechanics
Bending moment and shear force in statically determinate beams; Simple bending theory, flexural and shear stresses, shear centre; Uniform torsion, buckling of column, combined and direct bending stresses; Simple stress and strain relationships; Theories of failures.
Structural Analysis
Statically determinate and indeterminate structures by force/ energy methods; Method of superposition; arches, beams, cables, Analysis of trusses, frames; Displacement methods: Slope deflection and moment distribution methods; Influence lines; Stiffness and flexibility methods of structural analysis.
Construction Materials and Management
Construction Materials: Structural steel – composition, material properties, and behaviour; Concrete – constituents, mix design, short-term and long-term properties; Timber; Bitumen, Bricks and mortar. Construction Management: Types of construction projects; Tendering and construction contracts; Rate analysis and standard specifications; Cost estimation; Project planning and network analysis – CPM and PERT.
Concrete Structures
Working stress, Limit state, and Ultimate load design concepts; Design of columns, slabs, and beams; Bond and development length; Prestressed concrete; Analysis of beam sections at transfer and service loads.
Steel Structures
Working stress and Limit state design concepts; Connections – simple and eccentric, beam-column connections, plate girders and trusses; Design of tension and compression members, beams and beam-columns, column bases; Plastic Analysis of frames and beams.
GATE Geotechnical Engineering Syllabus 2025
Soil Mechanics
Origin of soils, soil structure, and fabric; Unified and Indian standard soil classification system; Three-phase system and phase relationships, index properties; Permeability – one-dimensional flow, Darcy’s law; Seepage through soils – two-dimensional flow, flow nets, uplift pressure, piping; Mohr’s circle, stress paths, practical and total shear strength parameters, characteristics of clays and sand of effective stress, capillarity, seepage force, and quicksand condition; One-dimensional consolidation, time rate of consolidation; Mohr’s circle, stress paths, practical and total shear strength parameters, characteristics of clays and sand; Compaction in laboratory and field conditions.
Foundation Engineering
Subsurface investigations – boreholes, drilling, scopes sampling, plate load test, standard penetration, and cone penetration tests; Earth pressure theories – Coulomb and Rankine; Stability of slopes finite and infinite slopes, method of slices and Bishop’s method; Contact pressure; Settlement analysis in sands and clays; Deep foundations – types of piles, static and dynamic formulae, load capacity of piles in sands and clays, pile load test, negative skin friction; Earth pressure theories – Rankine and Coulomb; Stability of slopes finite and infinite slopes, Bishop’s method of slices and Bishop’s method; Stress distribution in soils – Westergaards and Boussinesq’s theories, pressure bulbs; Shallow foundations – Terzaghi’s and Meyerhoff’s bearing capacity theories, the effect of the water table; Combined footing and raft foundation.
GATE Water Resource Engineering Syllabus 2025
Fluid Mechanics
Properties of fluids, fluid statics; Energy, momentum and continuity and corresponding equations; Potential flow, applications of momentum and energy equations; Turbulent and Laminar flow; Flow in pipes, pipe networks; Concept of boundary layer and its growth.
Hydraulics
Flow measurement in channels and pipes; Dimensional analysis and hydraulic similitude; Forces on Immersed bodies; Kinematics of flow, velocity triangles; Basics of hydraulic machines, specific speed of pumps and turbines; Channel Hydraulics – Energy-depth relationships, specific energy, slope profile, critical flow, hydraulic jump, uniform flow, and gradually varied flow.
Hydrology
Hydrologic cycle, precipitation, evaporation, evapotranspiration, watershed, infiltration, unit hydrographs, hydrograph analysis, flood estimation and routing, reservoir capacity, reservoir, channel routing, surface run-off models, groundwater hydrology – steady state well hydraulics and aquifers; Application of Darcy’s laws.
Irrigation
Duty, delta, estimation of evapotranspiration; Crop water requirements; Design of lined and unlined canals, spillways, headworks, gravity dams and; Design of weirs on the permeable foundation; Types of irrigation systems, irrigation methods; Drainage and Water logging; Canal regulation works, cross-drainage structures, outlets, and escapes.
GATE Environmental Engineering Syllabus 2025
Water and Wastewater
Quality standards, basic unit processes, and operations for water treatment. Drinking water standards, water requirements, basic unit operations, and unit processes for surface water treatment, and distribution of water. Sewage and sewerage treatment, quantity, and characteristics of wastewater. Effluent discharge standards. Domestic wastewater treatment, primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment of wastewater, the number of characteristics of domestic wastewater, and primary and secondary treatment. Unit operations and unit processes of sludge disposal and domestic wastewater.
Air Pollution
Types of pollutants, their sources and impacts, air pollution meteorology, air quality standards, and limits, and air pollution control.
Municipal Solid Wastes
Characteristics, generation, collection, and transportation of solid wastes, engineered systems for solid waste management (energy recovery, reuse/ recycle, treatment, and disposal).
Noise Pollution
Impacts of noise, permissible limits of noise pollution, measurement of noise, and control of noise pollution.
GATE Transportation Engineering Syllabus 2025
Transportation Infrastructure
Highway alignment and engineering surveys; Geometric design of highways – cross-sectional elements, sight distances, horizontal and vertical alignments; Geometric design of railway track; Airport runway length, taxiway, and exit taxiway design.
Highway Pavements
Highway materials – desirable properties and quality control tests; Design of bituminous paving mixes; Design factors for flexible and rigid pavements; Design of flexible pavement using IRC: 37-2012; Design of rigid pavements using IRC: 58-2011; Distresses in concrete pavements.
Traffic Engineering
Traffic studies on flow, speed, travel time – delay and O-D study, PCU, peak hour factor, parking study, accident study, and Analysis, Statistical Analysis of traffic data; Microscopic and macroscopic parameters of traffic flow, fundamental relationships; Control devices, signal design by Webster’s method; Types of intersections and channelization; Highway capacity and level of service of rural highways and urban roads.
GATE Geomatics Engineering Syllabus 2025
Principles of surveying
Errors and their adjustment; Maps – scale, coordinate system; Distance and angle measurement – Leveling and trigonometric leveling; Traversing and triangulation survey; Total station; Horizontal and vertical curves.
Photogrammetry – scale, flying height; Remote sensing – basics, platform and sensors, visual image interpretation; Basics of Geographical information system (GIS).
GATE Civil Engineering Subject-Wise Weightage
The subject-wise weightage varies every year, and candidates are advised to refer to the official GATE website for the latest updates. To prepare for the examination, candidates must have a thorough understanding of the concepts, practice the previous year’s question papers, and take mock tests to improve their time management and accuracy.
| Subject | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engg. Maths | 13 | 8 | 8 | 13 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 10 | 13 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| Geotechnical Engineering | 15 | 14 | 12 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 16 |
| Environmental Engineering | 10 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 13 |
| Transportation Engineering | 9 | 9 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 12 | 6 |
| Strength of Materials | 10 | 9 | 9 | 6 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 5 |
| FM & HM | 5 | 9 | 13 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 7 |
| Structural Analysis | 0 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| RCC | 8 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Surveying | 3 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| Hydrology | 7 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| Design of Steel Structures | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Irrigation | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Constru. Materials & Mgmt. | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 1 |
Most Scoring & High-Weightage Topics (Based on 2020–2025 Trends)
Over the past several years, analysis of previous GATE CE papers shows that some subjects and sub-topics recur regularly and carry significant marks. Here’s what tends to pay off best:
| Subject / Sub-field | What Usually Comes / Why It’s High Score |
|---|---|
| Structural Engineering / Structural Analysis & Design | Shear force & bending moment, moment distribution / slope-deflection, design of concrete and steel structures — highest weightage (often 15–20+ marks). |
| Geotechnical Engineering | Soil mechanics, consolidation, seepage, foundation & earth-pressure theory — reliable scoring area (≈ 12–16 marks). |
| Water Resources / Hydraulics / Fluid Mechanics & Hydrology | Topics like fluid statics, open channel flow, hydraulics — frequently asked. |
| Environmental Engineering | Water supply/treatment, wastewater, air pollution, waste management — moderate but consistent weightage. |
| Transportation Engineering | Highway engineering basics, traffic engineering, pavement design — often appears (though lower weight compared to geotech/structural). |
| Engineering Mathematics | Fundamental for many numerical-type questions; usually around 13% of total paper. |
| General Aptitude | Easy 15 marks — almost guaranteed if prepared. |
Takeaway: Historically, the “safe-bet high-yield” core fields in GATE CE are Structural, Geotechnical, Water/Fluid/Hydraulics, and Environmental + Transportation. Coupled with good scoring in Mathematics + Aptitude, one can secure a solid base.
What “Important Topics” Mean According to Syllabus + Past Papers
Based on aggregated data from multiple sources, these are the sub-topics you should ensure you definitely cover (given their recurrence in recent papers).
-
Structural: Bending moment & shear force diagrams, slope-deflection / moment distribution / matrix methods (for indeterminate structures), design of steel and concrete structures.
-
Geotechnical: Soil Mechanics (classification, compaction, consolidation, permeability, seepage), Foundation Engineering, Earth Pressure, Slope Stability.
-
Hydraulics / Water Resources: Fluid statics & dynamics, open channel flow, basic hydraulics, hydrology (unit hydrograph, water‐resources fundamentals).
-
Environmental: Water & wastewater treatment processes, air pollution fundamentals, solid waste concepts.
-
Transportation: Highway/traffic engineering basics, pavement design concepts, traffic flow fundamentals.
-
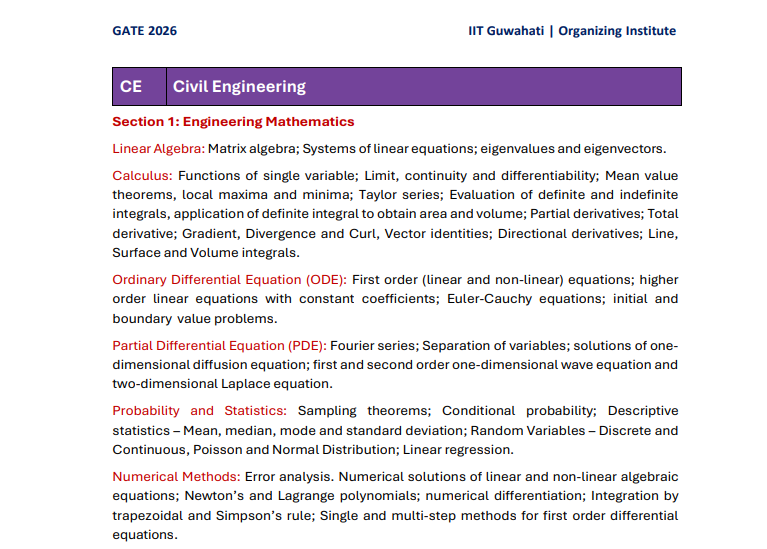
Maths: Linear Algebra, Calculus, Ordinary/Partial Differential Equations, Probability/Statistics, Numerical Methods — essential.
-
Aptitude: Verbal, Quantitative, Analytical reasoning — never skip.
Strategy: How to Prioritise Smartly (Given Time Constraints)
If you are preparing now (say few months before the exam), a balanced but efficient strategy would be:
-
Master: Structural + Geotechnical + Maths + Aptitude → these give the highest and most predictable returns.
-
Cover: Fluid/Hydraulics & Water-Resources, Environmental — these are moderate-scoring but often asked.
-
Attempt: Transportation & other smaller subfields (Geomatics/Surveying, Construction-management, etc.) depending on your comfort and time.
-
Revise & Practice PYQs: Solve many previous-year papers and mock tests. This helps understanding pattern, improves speed & accuracy, and avoids surprises.
GATE Civil Engineering Syllabus 2026 PDF
Get a Free PDF by clicking on the link below:
GATE CIVIL Engineering CE_2026_Syllabus
FAQs
Q1. What are the main sections/parts of the GATE CE 2026 syllabus?
A: The syllabus (for CE) broadly consists of:
-
Core civil-engineering subjects / core-discipline topics (Structural Engg, Geotechnical Engg, Water Resources & Fluid Mechanics, Environmental Engg, Transportation Engg, Geomatics/Surveying, Construction Materials & Management, etc.)
-
Engineering Mathematics (common for all branches
-
General Aptitude (GA) — Verbal, Quantitative, Analytical, and Spatial Aptitude.
Q2. What topics are included under Engineering Mathematics?
A: Important topics under Engineering Mathematics include:
-
Linear Algebra (matrix algebra, systems of linear equations, eigenvalues/eigenvectors)
-
Calculus (single-variable functions, limits/continuity/differentiability, mean-value theorems, Taylor series, definite/indefinite integrals, applications like area/volume, partial derivatives, vector calculus — gradient, divergence, curl, line/surface/volume integrals)
-
Ordinary Differential Equations (first-order, higher-order linear equations, Euler–Cauchy equations, initial/boundary value problems)
-
Partial Differential Equations (PDE): e.g. Fourier series, separation of variables, basic PDEs like diffusion, wave, Laplace’s equation etc.
-
Probability & Statistics, Numerical Methods (on many source sites)
Q3. Which are the major civil-engineering subject-areas I must focus on?
A: Major subject areas in CE with typical topics:
| Area | Topics / Sub-areas |
|---|---|
| Structural Engineering | Engineering mechanics (forces, equilibrium, free-body diagrams), solid mechanics (stress–strain, bending, shear, torsion, buckling), structural analysis (beams/trusses/frames, static/dynamic, energy methods, SFD/BMD, indeterminate structures). |
| Concrete & Steel Structures; Construction Materials & Management | Concrete design (limit-state working stress, beams/slabs/columns, prestressed concrete), steel structures (tension/compression members, beams, connections, plate girders/trusses), basic materials properties, mix design, project planning (PERT/CPM), cost & materials. |
| Geotechnical Engineering (Soil & Foundation) | Soil mechanics (soil properties, classification, behavior of sand/clay, permeability, compaction, consolidation, shear strength), foundation engineering (shallow and deep foundations, bearing capacity, settlement, pile foundations), seepage, slope stability, earth pressure theories. |
| Water Resources & Fluid Mechanics / Hydraulics | Fluid properties, fluid statics & dynamics, flow in pipes & channels, open-channel flow, hydrographs, irrigation fundamentals, canal/structure design, water requirements for crops, design of hydraulic structures (weirs, spillways), hydraulic jump, flow measurement & hydraulics principles. |
| Environmental Engineering | Water & wastewater treatment (treatment processes, quality standards, distribution systems, sewage design), air pollution basics & control (pollutants, standards, air quality index), municipal solid waste management (collection, disposal, recycling/reuse, energy recovery) etc. |
| Transportation Engineering | Highway / railway geometry & design (alignment, cross-section, sight distances), pavement design (flexible/rigid pavements), bituminous mixes, traffic engineering (traffic flow, speed, capacity, signal design, intersections), airport/runway/taxiway basics. |
| Geomatics / Surveying & Remote Sensing | Principles of surveying, distance & angle measurement, leveling, traversing, triangulation, total station, maps & coordinates, photogrammetry, remote sensing basics, GIS, horizontal/vertical curves. |
Q4. What is the role of General Aptitude (GA) in GATE CE 2026? What does it cover?
A: GA is a common section for all branches and contributes ~ 15 marks out of total.
GA covers four sub-domains:
-
Verbal Aptitude — English grammar, vocabulary, reading comprehension, sentence completion etc.
-
Quantitative Aptitude — numerical computation & estimation, data interpretation (tables, graphs), basic geometry & mensuration, elementary statistics & probability, ratios/percentages etc.
-
Analytical Aptitude — logical reasoning, analogies, deduction/induction, reasoning with numbers.
-
Spatial Aptitude — transformation of shapes (rotation, translation, scaling, mirroring), 2D/3D visualization, paper folding / pattern recognition / spatial reasoning.
Because GA has fixed marks, doing well here improves overall score — but many aspirants give more weight to core engineering topics.
Q5. How is the weightage distributed among different sections? Which areas are “high-priority”?
A: Based on the 2026 syllabus structure:
-
Core civil-engineering subjects together carry the majority of the weight (roughly 70–75%).
-
Engineering Mathematics typically contributes around 13–15%.
-
General Aptitude is ~ 15%.
-
Among civil topics, high-priority areas often are: Structural Engineering (including structural analysis, concrete & steel design), Geotechnical Engineering (soil/foundation), Water Resources & Fluid Mechanics / Hydraulics, Transportation, etc.