The OPRA Exam Syllabus 2026 Australia is designed to assess the knowledge, clinical competence, and professional skills of overseas-trained pharmacists seeking registration in Australia. Conducted by the Australian Pharmacy Council (APC), the exam ensures that international candidates meet Australian standards of pharmacy practice. The syllabus broadly covers biomedical sciences, pharmaceutical sciences, pharmacology, therapeutics, clinical pharmacy, ethics, and Australian healthcare regulations. It emphasizes patient-centered care, safe dispensing practices, and evidence-based decision-making. Understanding the OPRA syllabus thoroughly helps candidates plan focused preparation and improves their chances of successfully qualifying for pharmacist registration in Australia.
What Is the OPRA Exam?
The OPRA Exam (Overseas Pharmacist Readiness Assessment) is a licensing/skills assessment test conducted by the Australian Pharmacy Council (APC) for pharmacists who earned their qualifications outside Australia or New Zealand and now want to practice there.
This exam has replaced the older KAPS exam from March 2025 to better test clinical competence and real-world pharmacy skills rather than just theoretical knowledge.
Passing the OPRA exam is mandatory for international pharmacists before they can proceed with provisional registration and eventually full registration to practice in Australia.
OPRA Exam Pattern (Exam Structure)
Here’s what you need to know about how the exam is structured:
Format
-
Type: Multiple-choice questions (MCQs)
-
Mode: Computer-based
-
Total Questions: 120 questions
-
Duration: 2.5 hours (150 minutes)
-
Methodology: Adaptive Rasch testing model, difficulty adjusts based on your responses, and results reflect your competence rather than raw score thresholds.
Key Points
-
There is only 1 paper — no separate papers like in older assessments.
-
Questions often involve clinical case scenarios, prescription analysis, and practical problem-solving reflective of real pharmacy practice.
OPRA Exam Syllabus: Detailed Breakdown
The syllabus is divided into five main content areas, each representing a portion of the overall exam. These aren’t isolated textbook chapters — they emphasize application of knowledge within pharmacy care contexts.
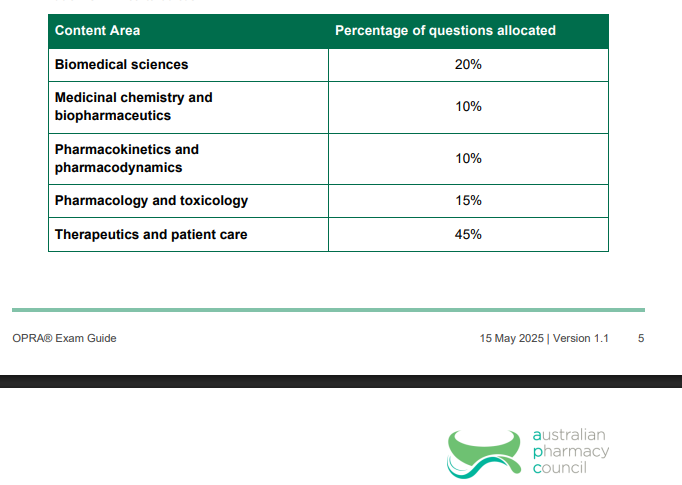
Syllabus Weightage & Topics
| Content Area | Approx. Weightage | What It Covers |
|---|---|---|
| Therapeutics & Patient Care | 45% | • Clinical scenarios & decision-making • Patient safety and medication management • Drug interactions & adverse effects • Pharmacotherapy planning |
| Biomedical Sciences | 20% | • Pathophysiology • Microbiology & immunology • Metabolism and physiology |
| Pharmacology & Toxicology | 15% | • Mechanisms of drug action • Side effects and toxicology • Drug classification & therapeutic outcomes |
| Pharmacokinetics & Pharmacodynamics | 10% | • Drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion • Dose-response relationships • Time-action profiles |
| Medicinal Chemistry & Biopharmaceutics | 10% | • Drug design and development • Formulation science & delivery systems • Chemical properties and bioavailability |
(The percentages above are based on the latest syllabus outlines and may be similar for 2026 cycles.)
What to Expect in Each Section
Therapeutics & Patient Care
This is the most important and largest section — nearly half the exam. You’ll face case studies requiring you to:
-
Evaluate patient symptoms and medical histories
-
Choose appropriate medication strategies
-
Identify harmful interactions or contraindications
-
Recommend counselling and monitoring plans
This section tests your clinical ability more than rote knowledge.
Biomedical Sciences
Look at how diseases affect the body, how pathogens work, and how immune systems respond. The focus is understanding disease processes so you can connect them with treatment decisions.
Pharmacology & Toxicology
Questions will ask about:
-
Drug effects on systems
-
Toxic dose responses
-
Adverse drug reactions
-
Safe use limits
This section bridges drug science with patient safety.
Pharmacokinetics & Pharmacodynamics
You should be comfortable with:
-
How the body processes drugs
-
Concepts like half-life and therapeutic window
-
Interpreting these for dose planning
This is more applied science than memorization.
Medicinal Chemistry & Biopharmaceutics
Expect questions on:
-
How drugs are designed and modified
-
How chemical properties influence absorption and delivery
-
Formulation choices in practice
These basics help you understand why certain drugs behave the way they do in patients.
Recommended Study Approach
Given the integrated and clinical nature of the test:
Study real-world case scenarios
Focus on therapeutic decision-making skills
Use clinical pharmacy textbooks and practice MCQs
Practice applying biomedical principles to patient situations
Unlike older exams, memorizing facts alone won’t guarantee success — you must connect science with practice.
Tips for 2026 Aspirants
-
Start early: Many candidates prepare for months in advance.
-
Focus on patients: Real clinical cases give you the best practice for this exam.
-
Use ethics and professional judgment: Some scenarios may test safe practice norms within Australian healthcare.
-
Mock exams help: They prepare you for Rasch adaptive testing and time management.
OPRA Exam Syllabus in Detail
-
Biomedical Sciences
The Biomedical Sciences section of the OPRA Exam forms the foundational pillar of pharmacy knowledge, focusing on the biological and physiological principles that underpin human health and disease. It encompasses human anatomy and physiology, where candidates learn how organ systems function and interact to maintain homeostasis. Pathophysiology explores how these systems are disrupted during illness, helping pharmacists understand disease mechanisms and clinical manifestations. Microbiology and immunology delve into infectious agents and the body’s defence mechanisms, covering topics like host-pathogen interactions, sterilization, and vaccination. Biochemistry and molecular biology round out the domain by examining the chemical processes within cells, including metabolism, enzyme activity, and genetic regulation—critical for understanding drug action and resistance. Together, these areas equip pharmacists with the scientific insight needed to interpret clinical scenarios and support safe, effective patient care.
-
Medicinal chemistry and biopharmaceutics
Medicinal chemistry and biopharmaceutics are critical components of the OPRA Exam syllabus, bridging the gap between drug design and its behaviour in the human body. Medicinal chemistry focuses on the chemical structure, properties, and synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds, emphasizing how molecular modifications influence drug activity, selectivity, and safety. It also explores structure-activity relationships (SAR), mechanisms of drug action, and resistance. Biopharmaceutics, on the other hand, examines how the physical and chemical properties of drugs, dosage forms, and formulation strategies affect absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME). It includes concepts like bioavailability, drug solubility, permeability, and the impact of excipients and delivery systems. Together, these disciplines equip pharmacists with the scientific understanding needed to optimize drug therapy and ensure effective patient outcomes.
-
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics are essential scientific principles that guide how drugs behave in the body and how they produce therapeutic effects. Pharmacokinetics focuses on the journey of a drug through the body—how it is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted (ADME). It helps pharmacists understand factors that influence drug concentration over time, such as bioavailability, half-life, and clearance. Pharmacodynamics, on the other hand, examines the drug’s biological effects and mechanisms of action at the cellular or receptor level. It explores dose-response relationships, therapeutic windows, and drug-receptor interactions. Together, these disciplines enable pharmacists to optimize dosing regimens, predict drug interactions, and ensure safe and effective patient care.
-
Pharmacology and toxicology
Pharmacology and toxicology are vital disciplines within the OPRA Exam that help pharmacists understand both the therapeutic and harmful effects of drugs. Pharmacology focuses on how drugs interact with biological systems to produce desired outcomes, covering mechanisms of action, drug classifications, dose-response relationships, and therapeutic uses. It equips pharmacists to select appropriate medications, monitor efficacy, and manage side effects. Toxicology, on the other hand, examines the adverse effects of chemicals and drugs on the body, including overdose, poisoning, and long-term exposure risks. It involves understanding toxic doses, antidotes, and safety margins. Together, these fields ensure pharmacists can balance efficacy with safety, prevent medication-related harm, and respond effectively to toxicological emergencies.
-
Therapeutics and patient care
Therapeutics and patient care form the heart of pharmacy practice, emphasizing the safe, effective, and compassionate use of medicines to improve health outcomes. In the OPRA Exam, this area focuses on applying clinical knowledge to real-world scenarios, including selecting appropriate drug therapies, monitoring treatment effectiveness, and managing side effects. It involves understanding disease-specific guidelines, tailoring treatments to individual patient needs, and promoting medication adherence. Patient care also includes clear communication, cultural sensitivity, and ethical decision-making—ensuring pharmacists can educate, support, and advocate for patients across diverse healthcare settings. This domain prepares candidates to deliver holistic, evidence-based care that prioritizes both clinical efficacy and patient well-being.
OPRA Exam Syllabus PDF Download Link
Get PDF of OPRA Exam Syllabus by click on the link OPRA Exam Syllabus
Summary
The OPRA Exam Syllabus 2026 is designed to ensure pharmacists can safely and effectively practice in Australia. Its focus has shifted from pure theory to clinical competence and patient-centered decision-making. By understanding and preparing in the five key areas — therapeutics, biomedical sciences, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and medicinal chemistry — you’ll be ready for this globally relevant exam.
FAQs
1. What is the OPRA Exam?
Q: What does OPRA stand for?
A: OPRA stands for Overseas Pharmacist Readiness Assessment. It is an exam conducted by the Australian Pharmacy Council (APC) to assess whether overseas-qualified pharmacists have the necessary biomedical and pharmaceutical sciences knowledge to practise safely in Australia or NZ.
2. Why is OPRA Important?
Q: Why must I pass the OPRA exam?
A: Passing OPRA is mandatory to obtain a Skills Assessment Outcome from APC. This outcome is required to support visa applications and to apply for provisional pharmacist registration with the Pharmacy Board of Australia (via AHPRA).
3. When and Where is the 2026 OPRA Exam Held?
Q: What are the exam dates in 2026?
A: APC runs multiple sessions in 2026. For example:
-
Jan–Feb registration → Mar exam
-
Apr–Jun registration → July exam
-
Aug–Oct registration → Nov exam
Results are released roughly 4 weeks after your test.
Q: Can I sit the exam outside Australia?
A: Yes — there are test centres globally, including in India, UK, Canada, Middle East, Africa, and more.
4. What is the OPRA Exam Format?
Q: What type of questions are on the exam?
A: It consists of 120 Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) delivered via computer.
Q: How long is the exam?
A: 2.5 hours (150 minutes).
5. What Does the Syllabus Cover?
The official OPRA syllabus is structured around five core content areas based on biomedical and pharmaceutical sciences:
Core Content Areas
| Content Area | Approx % Weightage |
|---|---|
| Biomedical Sciences | ~20% |
| Medicinal Chemistry & Biopharmaceutics | ~10% |
| Pharmacokinetics & Pharmacodynamics | ~10% |
| Pharmacology & Toxicology | ~15% |
| Therapeutics & Patient Care | ~45% |
(These percentages are approximations used for prep planning and reflect common breakdowns across study sources.)
6. What Topics Are Included in Each Section?
Biomedical Sciences
-
Normal & disease physiology
-
Pathophysiology
-
Microbiology & immunology
-
Electrolyte/fluids disorders
Medicinal Chemistry & Biopharmaceutics
-
ADME (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion)
-
Drug formulation & delivery
-
Stability & solubility
Pharmacokinetics & Pharmacodynamics
-
Drug metabolism and actions
-
Half-life, clearance, calculation concepts
-
Use of PK/PD data in therapy decisions
Pharmacology & Toxicology
-
Mechanisms of drug actions
-
Drug interactions and adverse effects
-
Toxicity and clinical management
Therapeutics & Patient Care
-
Dose calculation & adjustments
-
Primary care & OTC management
-
Special populations (children, elderly, pregnancy)
-
Health promotion & patient counselling
7. What Competencies Are Tested?
Q: Does OPRA test only knowledge recall?
A: No — questions are designed to assess a mix of remembering, understanding, and application, including clinical reasoning and safe patient care.
8. How Is the Exam Scored?
Q: What scoring method is used?
A: OPRA uses Rasch scaling methodology — a competency-based scoring system that accounts for question difficulty, not just correct answers.
Q: Is there negative marking?
A: There is no negative marking reported in official syllabus descriptions.
9. Do I Need to Know Australian Law/Ethics?
Q: Does the exam cover Australian pharmacy law and ethics?
A: Official OPRA syllabus focuses on biomedical and clinical sciences — it does not test specific Australian pharmacy legislation or professional regulations. These topics are assessed later during internship and registration stages.
10. Who Can Sit the Exam?
Q: Am I eligible to take the OPRA exam?
A: You must hold a pharmacy degree from outside Australia, NZ, UK, Canada, Ireland or the USA, and apply for an Eligibility Check through the APC Candidate Portal before registering for the exam.
11. Can I Re-sit the OPRA Exam?
Q: What if I fail?
A: Yes — you may sit the exam again in a later session, but you must pay the full exam fee each time.
12. How Long Is the Result Valid?
Q: After passing, how long is the Skills Assessment valid?
A: The Skills Assessment Outcome from OPRA is typically valid for 3 years toward registration and visa processes.
13. How Should I Prepare?
Q: What is the best way to study for the OPRA exam?
A: Preparation strategies include:
-
Building strong foundational knowledge in sciences
-
Practising case-based and clinical MCQs
-
Time-management drills (120 questions in 150 minutes)
-
Using official sample materials from APC