Rajasthan Judiciary Syllabus 2025: The Rajasthan Judiciary Exam is a prestigious state-level recruitment examination conducted by the Rajasthan High Court to appoint Civil Judges (Junior Division) in the state judicial services. With the 2025 exam cycle approaching, aspiring candidates must familiarize themselves with the detailed syllabus and exam pattern to streamline their preparation. The Rajasthan Judiciary Syllabus 2025 is designed to assess a candidate’s legal aptitude, general awareness, reasoning abilities, and language proficiency. The selection process comprises three stages: Preliminary Examination, Mains Examination, and Interview. The Prelims act as a screening test with objective-type questions based on law, English, and current affairs. The Mains is a descriptive test covering key legal subjects such as Civil Law, Criminal Law, and Language papers. Finally, the Interview round evaluates personality, communication skills, and suitability for the judicial role. Understanding the syllabus in depth is crucial for candidates to identify high-weightage topics and create an effective study plan. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the Rajasthan Judiciary Syllabus 2025, including subject-wise breakdowns, important topics, and preparation tips to help candidates navigate the exam with confidence and precision.
RJS Rajasthan Judiciary Syllabus and Exam Pattern 2025
The Rajasthan Judicial Services (RJS) Examination 2025 is structured into three stages: Preliminary Examination, Main Examination, and Interview. The syllabus has been updated to include new laws and acts, making it essential for aspirants to familiarize themselves with the latest content. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
RJS Preliminary Examination Exam Pattern (Objective Type)
-
Duration: 2 hours
-
Total Marks: 100
-
Question Type: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
-
Distribution:
-
Law Subjects: 70 questions (70 marks)
-
Hindi Proficiency: 15 questions (15 marks)
-
English Proficiency: 15 questions (15 marks)
-
Law Subjects (70% Weightage)
The law subjects for the Preliminary Examination align with those prescribed for Law Papers I and II in the Main Examination. Key topics include:
-
Code of Civil Procedure, 1908
-
Constitution of India
-
Indian Contract Act, 1872
-
Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), 2023 & Indian Penal Code, 1860
-
Bhartiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS), 2023 & Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973
-
Bhartiya Sakshya Adhiniyam (BSA), 2023 & Indian Evidence Act, 1872
-
Limitation Act, 1963
-
Specific Relief Act, 1963
-
Transfer of Property Act, 1882
-
Interpretation of Statutes
-
Rajasthan Rent Control Act, 2001
-
Hindu Law (Marriage, Adoption, Maintenance, Succession, Guardianship)
-
Mohammedan Law (Marriage, Divorce, Inheritance, Maintenance)
-
Information Technology Act, 2000
-
Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012
-
Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015
-
Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881
-
Probation of Offenders Act, 1958
-
Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005
-
Indecent Representation of Women (Prohibition) Act, 1986
-
Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013
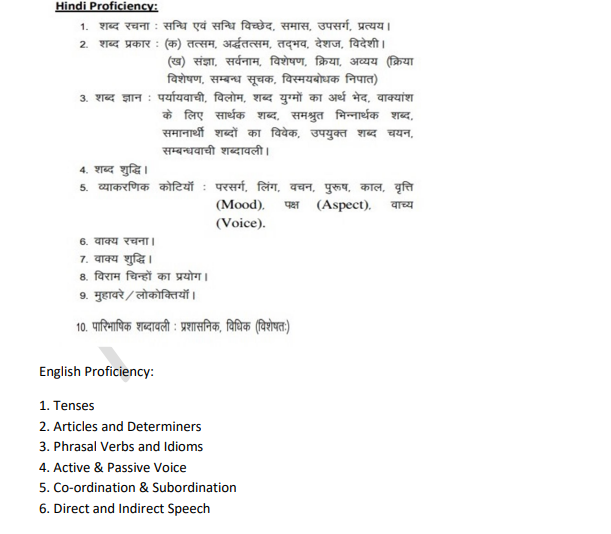
Hindi Proficiency (15% Weightage)
The Hindi section assesses grammar and vocabulary, including:
-
शब्द रचना: संधि, समास, उपसर्ग, प्रत्यय
-
शब्द प्रकार: तत्सम, तद्भव, विदेशी शब्द
-
व्याकरणिक कोटियाँ: लिंग, वचन, पुरुष, काल, वृत्ति, पक्ष, वाच्य
-
वाक्य शुद्धि, विराम चिन्ह, मुहावरे/लोकोक्तियाँ
-
विधिक एवं प्रशासनिक पारिभाषिक शब्दावली
English Proficiency (15% Weightage)
The English section evaluates grammar and comprehension, covering:
-
Tenses, Articles, Determiners
-
Phrasal Verbs & Idioms
-
Active & Passive Voice
-
Co-ordination & Subordination
-
Direct & Indirect Speech
-
Modals (Obligation, Request, Permission, etc.)
-
Antonyms & Synonyms
RJS Main Examination (Descriptive Type)
The Main Examination comprises four papers, each designed to assess the candidate’s legal knowledge and language proficiency.
Law Paper I
Focuses on civil law topics:
-
Code of Civil Procedure, 1908
-
Constitution of India
-
Indian Contract Act, 1872
-
Limitation Act, 1963
-
Specific Relief Act, 1963
-
Transfer of Property Act, 1882
-
Interpretation of Statutes
-
Rajasthan Rent Control Act, 2001
-
Hindu Law (Marriage, Adoption, Maintenance, Succession, Guardianship)
-
Mohammedan Law (Marriage, Divorce, Inheritance, Maintenance)
Law Paper II
Covers criminal law and related statutes:
-
Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), 2023 & Indian Penal Code, 1860
-
Bhartiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS), 2023 & Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973
-
Bhartiya Sakshya Adhiniyam (BSA), 2023 & Indian Evidence Act, 1872
-
Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015
-
Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881
-
Probation of Offenders Act, 1958
-
Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005
-
Indecent Representation of Women (Prohibition) Act, 1986
-
Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012
-
Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013
-
Framing of Charge/Judgment Writing
Language Papers
-
Paper I: Hindi Essay (50 Marks, 2 Hours)
-
Paper II: English Essay (50 Marks, 2 Hours)
These papers assess the candidate’s ability to articulate thoughts clearly and coherently in both Hindi and English.
Interview (Viva-Voce)
-
Total Marks: 35
-
Assessment Criteria:
-
Academic record
-
Character and personality
-
Communication skills
-
General knowledge and current affairs
-
Suitability for judicial service
-
Rajasthan Judiciary RJS Syllabus: FAQs
1. What is the structure of the RJS exam?
The RJS exam comprises three stages:
-
Preliminary Examination: Objective-type test with 100 questions, lasting 2 hours.
-
Mains Examination: Descriptive written exam with four papers.
-
Interview (Viva-Voce): Personal interview carrying 35 marks.
Note: The Preliminary exam is qualifying in nature; its marks are not counted in the final merit.
2. What subjects are covered in the Preliminary exam?
The Preliminary exam includes:
-
Law Subjects (70% weightage): Civil and Criminal Law topics.
-
Language Proficiency (30% weightage): Hindi and English language skills.
Note: There is no negative marking in the Preliminary exam.
3. What are the components of the Mains exam?
The Mains exam consists of four descriptive papers:
-
Law Paper I (Civil Law): 3 hours, 100 marks.
-
Law Paper II (Criminal Law): 3 hours, 100 marks.
-
Hindi Essay: 2 hours, 50 marks.
-
English Essay: 2 hours, 50 marks.
Note: Judgment writing and charge framing are integral parts of the Law papers.
4. What is the syllabus for Law Papers in the Mains exam?
Law Paper I (Civil Law) includes:
-
The Constitution of India
-
Code of Civil Procedure, 1908
-
Indian Contract Act, 1872
-
Specific Relief Act, 1963
-
Transfer of Property Act, 1882
-
Limitation Act, 1963
-
Rajasthan Rent Control Act, 2001
-
Judgment Writing
Law Paper II (Criminal Law) includes:
-
Indian Penal Code, 1860
-
Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973
-
Indian Evidence Act, 1872
-
Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005
-
Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015
-
Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 (Chapter XVII)
-
Probation of Offenders Act, 1958
-
Framing of Charge and Judgment Writing
Note: The syllabus has been updated to include new laws such as the Bhartiya Nyay Sanhita, 2023, replacing parts of the Indian Penal Code.
5. What is the focus of the Language Papers in the Mains exam?
-
Hindi Essay: Essay writing on legal, social, and contemporary issues in Hindi.
-
English Essay: Essay writing on legal, social, and contemporary issues in English.
Note: Proficiency in essay writing, grammar, and vocabulary is essential.
6. What does the Interview stage assess?
The Interview (Viva-Voce) carries 35 marks and evaluates:
-
Legal knowledge and understanding.
-
Communication skills and personality.
-
Awareness of current affairs and social issues.
Note: Confidence, ethical judgment, and knowledge of Rajasthan’s legal and social landscape are crucial.
7. What are the minimum qualifying marks for the exams?
-
Preliminary Exam:
-
General/OBC/MBC/EWS: 45%
-
SC/ST/PwD/Ex-Servicemen: 40%
-
-
Mains Exam: Candidates must score sufficiently high marks to be shortlisted for the Interview.
Note: Only those who qualify in the Preliminary exam are eligible to appear for the Mains exam.