CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book Keeping and Accountancy Syllabus 2025-26 is released by the CBSE Board. Now Students have begun completing their class work, home work as well and started preparing for the final exams. If you’re looking for the CBSE Class 10 Element of Book Keeping Syllabus 2025-26, don’t worry, we’ve got it for you. Check out the latest syllabus for Elements of Bookkeeping and Accountancy here.
CBSE Class 10 Element of Book Keeping Syllabus 2025-26
The CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book Keeping and Accountancy syllabus for the academic year 2025-26 is designed to introduce students to the fundamentals of financial accounting. It covers essential topics such as accounting terminology, principles, and practices, along with the preparation and maintenance of financial records. The syllabus aims to develop a strong foundation in book-keeping, enabling students to understand and apply basic financial concepts in real-life scenarios. This course is crucial for those planning to pursue commerce in higher education, offering a practical approach to managing personal and business finances.
Elements of Bookkeeping and Accountancy Course Structure
The Course Structure of Class 10 Element of Bookkeeping and Accountancy Course is given below.
|
Unit
|
Contents
|
Marks
|
Periods
|
|
1
|
Capital and Revenue
|
8
|
25
|
|
2
|
Depreciation
|
12
|
35
|
|
3
|
Bank Reconciliation Statement
|
14
|
45
|
|
4
|
Bills of Exchange
|
10
|
25
|
|
5
|
Final Accounts
|
14
|
45
|
|
6
|
Accounting from Incomplete Records
|
12
|
35
|
|
Total
|
70
|
210
|
|
|
Project
|
30
|
30
|
Class 10 Element of Book Keeping Syllabus 2026 Unit wise
Unit 1: Capital and Revenue
|
Content
|
Learning Outcomes
|
|
Capital and revenue: Capital and revenue receipts, capital and revenue expenditure and deferred revenue expenditure
|
The learners would be able to :
● Recapitulate the meaning of the terms ‘Capital’ and ‘Revenue’
● Appreciate the difference between capital and revenue receipts and capital and revenue expenditure
● Acquire knowledge about deferred revenue Expenditure
|
Unit 2: Depreciation
|
Content
|
Learning Outcomes
|
|
Depreciation: Need and methods of charging depreciation-straight line and Diminishing balance method (no change in the method)
|
The learners would be able to :
● Explain the necessity of providing depreciation on fixed assets
● Develop the skill of using the different methods
i.e. straight line and diminishing balance for computing depreciation
● Prepare fixed assets accounting using straight line and diminishing balance method of charging
depreciation
|
Unit 3: Bank Reconciliation Statement
|
Content
|
Learning Outcomes
|
|
Bank Reconciliation Statement: Meaning Preparation of BRS with the given cash book/pass book balance
|
The learners would be able to :
● Understand the concept of bank reconciliation statement
● Appreciate the need to prepare a bank reconciliation statement
● Develop an understanding of preparing bank reconciliation Statement
|
Unit-4: Bills Of Exchange
|
Content
|
Learning Outcomes
|
|
Bill of Exchange: Nature and use of Bills of Exchange, Terms used in Bills of Exchange. Simple transactions related to bills of exchange (No dishonour, retiring & renewal of the bill)
|
The learners would be able to :
● Acquire the knowledge of using bills of exchange for financing business transactions
● Understand the need for Bills of exchange in business
● State the meaning of different terms used in bills of exchange and their implication in accounting
● Develop the skill of journalising simple bill transactions in the book of creditor and debtor
|
Unit 5: Final Accounts
|
Content
|
Learning Outcomes
|
|
Final Accounts: Preparation of Trading and Profit & loss Account and Balance Sheet of Sole trader.
Adjustment for closing stock only. [amount of closing stock to be given]
|
The learners would be able to :
● State the meaning of financial statements & the purpose they serve for a sole proprietor.
● Develop the skill of preparing Trading Accounts and calculating gross profit.
● Develop the skill of preparing a Profit & Loss Account and calculating the net profit
● Explain the need for preparing a ‘Balance Sheet’.
● Understand the techniques of preparing the ‘Balance Sheet’.
● Develop an understanding of the simple adjustment for closing stock
|
Unit 6: Accounting from Incomplete Records
|
Content
|
Learning Outcomes
|
|
Accounting from Incomplete Records: Meaning; preparation of statement of Profit, statement of affairs. [statement of affairs method only]
|
The learners would be able to :
● State the meaning of incomplete records
● Understand the uses and limitations of incomplete records
● Develop the skill of computation of profit/loss by preparing a Statement of Profit
● Develop the skill of preparing a statement of
Affairs and ascertain the position of the business on a particular date.
|
Latest Elements of Book–Keeping and Accountancy (CODE NO. 254) CLASS–X (2026)
One Paper 3 Hours 70 Marks 210 Periods
Unit 1: Capital and Revenue 25 Periods 08 Marks
Content Learning Outcomes
Capital and revenue : Capital and revenue receipts,
capital and revenue expenditure and deferred revenue expenditure The learners would be able to :
● Recapitulate the meaning of the terms ‘Capital’ and ‘Revenue’
● Appreciate the difference between capital and revenue receipts and capital and revenue expenditure
● Acquire the knowledge about deferred revenue Expenditure
Content Learning Outcomes Depreciation : Need and methods of charging depreciation–straight line and Diminishing balance method (no change in the method) The learners would be able to :
● Explain the necessity of providing depreciation on fixed assets
● Develop the skill of using the different methods i.e. straight line and diminishing balance for computing depreciation
● Prepare fixed assets accounting using straight line and diminishing balance method of charging depreciation
Unit 3: Bank Reconciliation Statement 45 Periods 14 Marks
Content Learning Outcomes Bank Reconciliation Statement : Meaning Preparation of BRS with the given cash book / pass
book balance The learners would be able to :
● Understand the concept of bank reconciliation statement
● Appreciate the need of preparing bank reconciliation statement
● Develop understanding of preparing bank reconciliation Statement
Content Learning Outcomes
Bill of Exchange : Nature and use of Bills of Exchange, Terms used in Bills of Exchange. Simple transactions related to bills of exchange (No
dishonour, retiring & renewal of the bill) The learners would be able to :
● Acquire the knowledge of using bills of exchange for financing business transactions
● Understand the need of Bills of exchange in business
● State the meaning of different terms used in bills of exchange and their implication in accounting
● Develop in the skill of journalising simple bill transactions in the book of creditor and debtor
Unit 5: Final Accounts 45 Periods 14 Marks
Content Learning Outcomes
Final Accounts : Preparation of Trading and Profit & loss Account and Balance Sheet of Sole trader.
Adjustment for closing stock only. [amount of closing stock to be given]
The learners would be able to :
● State the meaning of financial statements & the purpose they serve for a sole proprietor.
● Develop the skill of preparing Trading Account and calculating gross profit.
● Develop the skill of preparing Profit & Loss Account and calculating the net profit
● Explain the need for preparing ‘Balance Sheet’.
● Understand the techniques of preparing the ‘Balance Sheet’.
● Develop the understanding to the simple adjustment for closing stock
Unit 6: Accounting from Incomplete Records 35 Periods 12 Marks
Content Learning Outcomes
Accounting from Incomplete Records : Meaning; preparation of statement of Profit, statement of affairs. [statement of affairs method only]
The learners would be able to :
● State the meaning of incomplete records
● Understand the uses and limitations of incomplete records
● Develop the skill of computation of profit / loss by preparing Statement of Profit
● Develop the skill of preparing ‘Statement of Affairs’ and ascertain the position of the business on a particular date.
Project Work
Project – I 15 Periods 15 Marks
Identify 20 items and classify them as capital and revenue receipts, capital and revenue expenditure and deferred revenue expenditure
(OR any other topic related to the course content)
Project –II 15 Periods 15 Marks
Make a statement of affairs for incomplete records of a small shop. (OR any other topic related to the course content)
The CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education) Class 10 Book Keeping and Accountancy syllabus for the academic year 2024-25 focuses on equipping students with fundamental knowledge of financial accounting principles and book-keeping practices. This subject lays the groundwork for further studies in commerce and business, particularly in fields related to finance, accounting, and business administration.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the syllabus, covering all the key topics included for the academic year 2024-25:
CBSE Class 10 Element of Book Keeping Detailed Topics
Accounting as a Source of Information
- Concept of Accounting: Introduction to accounting, its objectives, importance, and role in financial decision-making.
- Users of Accounting Information: Identification of different stakeholders who use accounting information, such as investors, management, creditors, employees, and regulatory agencies.
- Branches of Accounting: Financial accounting, management accounting, cost accounting, etc.
Basic Accounting Terms
- Key Terminologies: Understanding terms like capital, liabilities, assets, revenue, expenses, profits, losses, drawings, etc.
- Transactions: Concept of business transactions, capital expenditure, revenue expenditure.
Accounting Principles
- GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles): Understanding the fundamental accounting principles such as:
- Business Entity Concept
- Going Concern Concept
- Money Measurement Concept
- Accrual Concept
- Dual Aspect Concept (Accounting Equation)
- Matching Concept
- Prudence/Conservatism
- Accounting Standards: An overview of the standard rules and guidelines followed in preparing accounts.
Journal
- Journal Entry: Introduction to double-entry bookkeeping, rules of debit and credit, and recording financial transactions.
- Format of Journal: Understanding the journal format and its columns such as Date, Particulars, L.F. (Ledger Folio), Debit, and Credit.
- Types of Journals: Special journals for different types of transactions like cash journal, purchase journal, sales journal, etc.
Ledger
- Concept and Significance of Ledger: The ledger is considered the principal book of accounts, with all journal entries posted into it.
- Posting from Journal to Ledger: Understanding the process of transferring journal entries to appropriate ledger accounts.
- Format of Ledger: Debit side, credit side, and balancing of ledger accounts.
Cash Book
- Types of Cash Books:
- Single column cash book (for cash transactions only).
- Double column cash book (for cash and bank transactions).
- Triple column cash book (for cash, bank, and discount transactions).
- Petty Cash Book: The concept of maintaining a petty cash book for minor expenses and its format.
- Imprest System: The system of maintaining petty cash by having a fixed amount replenished periodically.
Trial Balance
- Objective of Trial Balance: A trial balance is prepared to check the arithmetical accuracy of the ledger postings.
- Preparation of Trial Balance: Understanding the format of the trial balance and how it is derived from the ledger accounts.
- Errors Revealed and Not Revealed by Trial Balance: Types of errors detected by the trial balance such as errors of omission, commission, etc.
Depreciation
- Concept of Depreciation: The systematic allocation of the cost of a tangible fixed asset over its useful life.
- Methods of Depreciation:
- Straight Line Method
- Written Down Value Method
- Factors Influencing Depreciation: The cost of the asset, estimated useful life, and residual value.
Final Accounts
- Components of Final Accounts:
- Trading Account
- Profit and Loss Account
- Balance Sheet
- Preparation of Final Accounts: Process of preparing final accounts from a trial balance, including adjustments for closing stock, outstanding expenses, prepaid expenses, etc.
Bank Reconciliation Statement
- Meaning and Importance: A statement prepared to reconcile the balance of cash book and passbook (bank statement) and to locate differences between them.
- Causes of Differences: Understanding reasons for differences between bank and cash book balances, such as cheques issued but not yet presented, deposits not credited, and errors.
Accounting of Non-Trading Organizations
- Introduction to Non-Profit Organizations: Understanding the concept of non-profit entities such as clubs, societies, educational institutions, and their accounting practices.
- Receipts and Payments Account: A summary of cash receipts and payments during a particular period.
- Income and Expenditure Account: This account is equivalent to a profit and loss account, prepared by non-profit organizations to ascertain surplus or deficit.
- Balance Sheet of Non-Trading Organizations: Understanding how the balance sheet is prepared for non-trading concerns.
Assessment
For the 2024-25 academic year, the syllabus is generally split between theory and practical components. The assessment can include:
- Theory Exams: Based on the topics detailed above, generally focusing on the concepts, principles, and practical understanding of bookkeeping.
- Internal Assessment: Schools might conduct internal assessments including projects, practical exercises, and viva voce, where students will have to apply their learning.
CBSE Class 10 Element Of Book Keeping and Accounting 2025-26 PDF
You can download the PDF for the CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book Keeping and Accounting syllabus for the 2025-26 session from the official CBSE website. The syllabus covers key topics like Capital and Revenue, Depreciation, Bank Reconciliation Statements, Bills of Exchange, Final Accounts, and Accounting from Incomplete Records. Additionally, project work is included to enhance practical understanding.
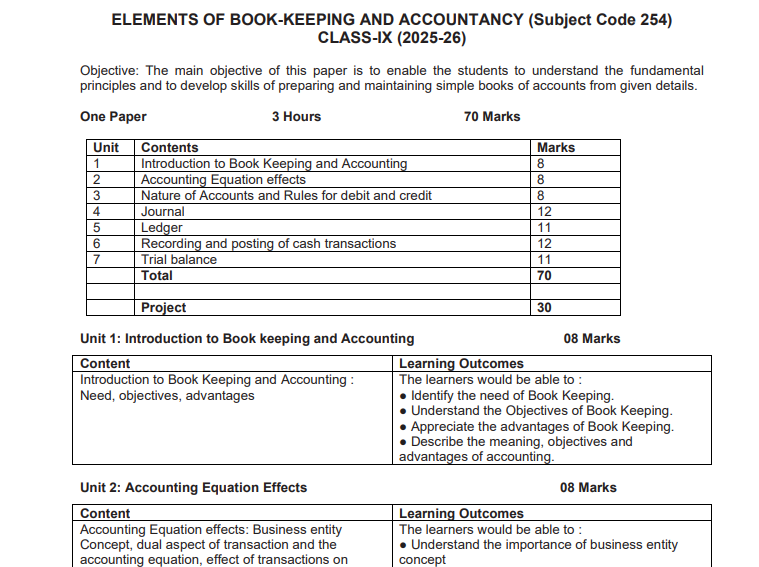
Elements_of_BK_Acc_Sec_2025-26
How to prepare CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book Keeping Syllabus for Board exams?
To prepare effectively for the CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book Keeping (part of the Accountancy syllabus), here is a structured approach to follow for the 2025-26 academic year:
Know the Syllabus
- Topics Overview: Get familiar with the syllabus provided by CBSE. The major topics include:
- Introduction to Book Keeping
- Basic Accounting Terms
- Theory of Accounting
- Books of Accounts
- Journal and Ledger
- Trial Balance
- Financial Statements
- Weightage of Topics: Check the weightage of each topic from previous years to prioritize the preparation of key areas.
Divide the Syllabus into Topics
Break down the syllabus into smaller, manageable sections:
- Unit 1: Introduction to Book Keeping
Understand basic concepts such as business transactions, accounting principles, and rules of debit and credit. - Unit 2: Journal and Ledger
Learn how to record transactions in the journal and post them to the ledger. - Unit 3: Trial Balance
Understand how to prepare a trial balance to verify the arithmetical accuracy of books. - Unit 4: Financial Statements
Focus on preparing trading accounts, profit and loss accounts, and balance sheets.
Follow a Time-Table
- Set aside specific time slots each day for book-keeping practice.
- Allocate more time for difficult topics, such as Journal entries, Trial Balance, and Financial Statements.
- Review and revise regularly to reinforce concepts.
Use NCERT Textbook and Reference Books
- Stick to the NCERT book as it is directly aligned with the syllabus.
- For extra practice, use reference books like TS Grewal and K.K. Gupta to get more practice questions.
Practical Application
- Practice problems on journalizing, posting to the ledger, and preparing trial balances and financial statements.
- Hands-on Practice: Set aside time to solve previous years’ question papers and sample papers regularly to become comfortable with the exam format.
Use Online Resources
- Watch online tutorials on accounting concepts, such as YouTube channels or apps like Byju’s and Khan Academy.
- Join online forums or groups to solve doubts and share notes.
Revision Strategy
- Weekly Revision: Review your progress and revise key topics.
- Monthly Mock Tests: Simulate exam conditions by attempting full-length mock tests.
- Focus on important chapters before exams and make quick reference notes for formulas or concepts that require memorization.
Time Management During the Exam
- While solving the paper, make sure to manage your time well, especially for practical questions.
- Focus on writing clear and concise answers.
By adhering to this plan, staying consistent, and revising frequently, you can prepare thoroughly for the CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book Keeping syllabus.
Best Books for CBSE Class 10 Accounts Syllabus
The best books and study materials you can use to prepare effectively for the CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book-Keeping and Accountancy syllabus (Accountancy Subject) in India. CBSE’s Accountancy syllabus covers topics such as Capital & Revenue, Depreciation, Bank Reconciliation Statement, Bills of Exchange, Final Accounts, and Accounting from Incomplete Records.
1. NCERT Textbook (Recommended Primary Resource)
-
CBSE does not prescribe an official NCERT book for Class 10 Accountancy, but CBSE syllabus and official sample papers act as primary reference for concepts and topics.
-
Always start with CBSE syllabus and sample questions from CBSE’s academic site to understand what is expected in exam.
2. Best Reference & Guide Books for Class 10 Accounts
These books are written specifically for the Class 10 Accounts syllabus:
Elements of Book-Keeping & Accountancy — Class 10 Guide
-
Provides detailed chapter-wise explanations, solved examples and practice questions tailored to CBSE Level.
Elements of Book-Keeping & Accountancy PYQ/Practice Books
-
Books compiling last years’ board questions and practice papers for Class 10 Accounts.
-
These help with pattern awareness and scoring in board exams.
3. Question Banks & Sample Papers
Practising questions is crucial for Accountancy:
Oswaal Books CBSE Accountancy Question Bank Class 10
-
Collections of chapter-wise and topic-wise questions.
-
Good for practice, MCQs, short answer and long answer questions.
(Oswaal is a recognized publisher of CBSE competitive preparation books)
CBSE Official Sample Papers + Past Year Papers
-
Download directly from the CBSE site or official releases.
-
These are extremely useful for understanding the exam style and key topics.
4. Additional Practice Resources
Aside from standard guides:
-
MCQ and Practice Workbooks for Elements of Book-Keeping & Accountancy help strengthen objective-type question skills.
-
Online mock tests/quizzes from reputable exam prep sites also help in revision.
Class 10 Element Of Book Keeping and Accounting: FAQs
1. What are the key topics covered in the CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book Keeping and Accounting syllabus?
- The major topics in the syllabus include:
- Introduction to accounting and its importance
- Accounting equation and journal entries
- Ledger posting and trial balance
- Cash book and bank reconciliation statement
- Depreciation, provisions, and reserves
- Final accounts: preparation of profit and loss account and balance sheet
2. Is the subject of Book Keeping and Accounting theory-based or practical?
- The subject combines both theory and practical components. Students need to understand fundamental concepts and also practice preparing financial statements, journal entries, ledger accounts, and trial balances. Theoretical concepts are tested alongside practical application.
3. What is the exam pattern for CBSE Class 10 Book Keeping and Accounting?
- The exam typically consists of two parts:
- Theory Paper: 80 marks
- Internal Assessment/Practical Work: 20 marks The theory paper includes both short and long-answer type questions, case-based questions, and numericals related to financial statements and journal entries.
4. Are there any important tips to score well in the Book Keeping and Accounting exam?
- Practice regularly: Keep practicing journal entries, ledger balancing, and preparing financial statements.
- Understand concepts: Focus on understanding the fundamental concepts instead of just memorizing.
- Work on presentation: Be clear and concise in solving numericals, and ensure neatness in final accounts.
- Review sample papers: Solve sample papers and previous years’ question papers to get a clear idea of the exam pattern and important topics.
5. Where can students find resources for Class 10 Book Keeping and Accounting preparation?
- Students can refer to:
- NCERT textbooks prescribed by CBSE.
- CBSE sample papers and previous years’ question papers.
- Online resources such as CBSE e-learning portals, YouTube tutorials, and revision notes.

1 thought on “CBSE Class 10 Element of Book Keeping Syllabus 2025-26, PDF Download”