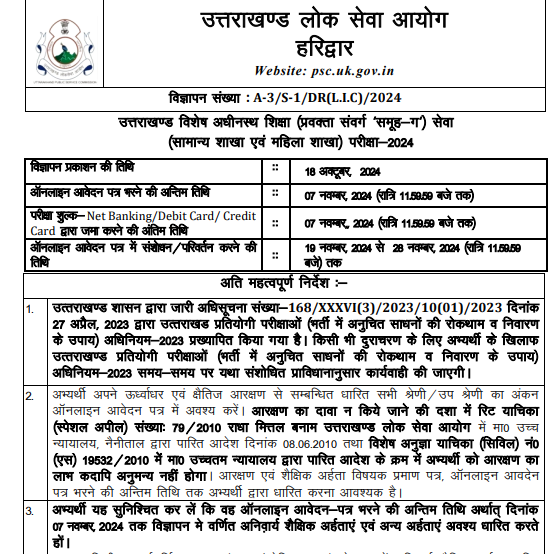
The UKPSC Lecturer Syllabus 2026 plays a crucial role for candidates preparing for the Uttarakhand Public Service Commission (UKPSC) Lecturer Examination. Conducted by the UKPSC, this exam aims to recruit skilled and knowledgeable lecturers for government intermediate colleges across Uttarakhand. The syllabus is carefully designed to assess a candidate’s subject expertise, teaching aptitude, and understanding of general awareness. It is divided into two main parts – General Studies and Subject-specific papers.
The General Studies section evaluates the candidate’s knowledge of current affairs, Indian history, geography, polity, economy, general science, and the culture of Uttarakhand. On the other hand, the Subject Paper focuses on the candidate’s specialization, testing their in-depth understanding, conceptual clarity, and ability to apply knowledge effectively. Each subject, whether it’s English, Hindi, Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics, or Political Science, follows a detailed and well-structured syllabus aligned with the state education board’s standards.
UK lecturer Syllabus 2026
Understanding the complete UKPSC Lecturer Syllabus 2026 is essential for building a focused preparation strategy. It helps aspirants identify key topics, manage time efficiently, and enhance their chances of securing a lecturer position in Uttarakhand’s reputed educational institutions.
UKPSC Lecturer Syllabus 2026
Detailed overview of the syllabus & exam pattern for the Uttarakhand Public Service Commission (UKPSC) Lecturer 2026 recruitment. Note: “all subjects” means the pattern is common for all Lecturer posts, but the subject‐knowledge / applied subject part will depend on the specific discipline (Hindi, English, History, Chemistry, etc.). The published syllabus for each specific discipline may vary and should be checked in the official notification.
UKPSC Lecturer Exam Pattern 2026
According to available sources, the pattern for Lecturer posts is as follows:
-
The selection consists of a written examination (Screening test + Subject‐Knowledge test) plus further stages (document verification etc.).
-
Screening / General Test: This is on Teaching Aptitude / General Awareness / General Intelligence etc.
-
Subject Knowledge Test (Concerned Discipline): Objective questions on the relevant subject opted by the candidate.
Example Pattern (for Polytechnic Lecturer) – can act as a reference:
| Paper | Subject | No. of Questions | Max Marks | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper 1 | General Hindi | 100 | 100 | 2 hours |
| Paper 2 | General English (only for certain subjects like Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics, Modern Office Management…) | 100 | 100 | 2 hours |
| Paper 3 | Concerned Subject / Applied Subject | 150 | 300 | 3 hours |
Note: Negative marking is mentioned in some sources: “1/4th mark for each wrong answer”.
UKPSC Lecturer Syllabus – Common/Core Sections
A) General Hindi
Typical topics include (for Paper 1 as per Polytechnic Lecturer version).
-
व्याकरण (Grammar)
-
संधि विच्छेद
-
विलोम शब्द, पर्यायवाची शब्द
-
वाक्यांशों के लिए एक शब्द
-
लिंग, समश्रुत-भिन्नार्थक शब्द
-
मुहावरे-लोकोक्तियाँ
-
सामान्य अशुद्धियाँ
-
लेखक-रचनाएँ (गद्य एवं पद्य)
B) General English
Common topics listed:
-
Terms commonly used in official communication
-
Direct & Indirect Narration
-
Voice
-
Articles, Adjectives, Adverbs, Conjunctions, Question tags
-
Synthesis: Simple, Compound & Complex Sentences
-
Correct use of Tenses
-
One word substitution; Synonyms, Antonyms, Homonyms
-
Prepositions; Subject-verb agreement; Correction of sentences
-
Idioms and Phrasal Verbs
-
Comprehension: Passage on scientific/technical theme, testing vocabulary, thematic understanding, fundamentals of grammar
C) Teaching Aptitude / General Awareness / General Intelligence
This is more for the Screening Test. Example syllabus:
-
Teaching Aptitude: general pedagogy, role of teacher, methods of teaching, educational psychology (often common in lecturer tests)
-
General Awareness: natural & economic resources (water, forests, wildlife, agriculture, horticulture), state & district administrative structure, recent movements, industrial/hydroelectric development of Uttarakhand, etc.
-
General Intelligence/Test of Reasoning: Percentage, Ratio & Proportion, Simple & Compound Interest, Profit & Loss, Time & Work, Time & Distance, HCF/LCM; analogies, syllogisms, missing numbers, characters & sequences, direction sense, coding-decoding; data representation (mean, median, mode, range)
3. Subject-Wise / Discipline Syllabus
Since the Lecturer posts cover multiple subjects (Hindi, English, History, Commerce, Maths, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Geography, etc), each subject will have its own detailed syllabus for the Subject Knowledge Test. The key points:
-
The concerned discipline paper will test deep knowledge of that particular subject.
-
For example: For the Mechanical Engineering subject (in the Polytechnic Lecturer variant) topics like Statics & Dynamics, Kinematics of rigid bodies, Work & Energy, etc.
-
For non-engineering subjects too, there are subject-specific Syllabus PDFs.
UK PSC Lecturer Subject-wise Syllabus 2026
1. Hindi
-
हिन्दी साहित्य का इतिहास । प्रारंभिक हिंदी काव्य, भक्तिकालीन कविता, लयबद्ध हिंदी कविता etc.
-
व्याकरण: सन्धि, समास, वचन-लिंग, वाक्य परिवर्तन, मुहावरे-लोकोक्तियाँ, एक-शब्दिक आदि.
-
लेखन-कला: पत्र लेखन, रिपोर्ट लेखन, अनुवाद (हिंदी↔अंग्रेजी) आदि.
2. English
-
Official communication terms; direct/indirect narration; voice; articles, adjectives, adverbs; clauses; tenses; one‐word substitution; synonyms/antonyms; prepositions; subject‐verb agreement; idioms & phrasal verbs; comprehension.
-
For the subject‐paper (concerned English lecturer) the syllabus will expand to English Literature, criticism, major works in English, etc. (Refer to detailed subject‐notification)
3. History
-
Ancient, medieval and modern Indian history: e.g., major dynasties, British rule, independence movement.
-
World history: industrial revolution, world wars, decolonization, political ideologies.
-
History of Uttarakhand (if state‐specific) may also be included.
4. Commerce
-
Fundamental concepts of commerce: business environment, trade, accounting, financial management, marketing, economics of business.
-
For UKPSC Lecturer, the subject paper will test in‐depth knowledge of commerce discipline. (Detailed topics will come in the subject‐notification)
5. Mathematics
-
Core mathematics topics: algebra, calculus, geometry, trigonometry, statistics, probability, discrete mathematics, teaching methodology of mathematics.
-
Also teaching aptitude/subject‐specific pedagogy may be included. For pattern see general subject‐paper pattern.
6. Physics
-
Core physics topics: mechanics, electromagnetism, thermodynamics, optics, modern physics, atomic & nuclear physics, solid state, etc.
-
Also lab methods, experiments, teaching methods in physics.
7. Chemistry
-
Physical chemistry (thermodynamics, kinetics, equilibrium), inorganic chemistry (periodic table, coordination compounds), organic chemistry (reaction mechanisms, biomolecules), analytical methods, applied chemistry.
-
Practical/experimental understanding and pedagogy may also be tested.
8. Biology
-
Botany & Zoology: cell biology, genetics, evolution, physiology (plant & animal), ecology, biodiversity, microbiology, biotechnology.
-
Also human biology, environment, conservation, teaching methods in biology.
9. Geography
-
Physical geography: landforms, climate, vegetation, soils, hydrology.
-
Human geography: population, migration, urbanisation, economic geography, resources, industry.
-
Indian geography: relief, drainage, agriculture, minerals, transport network. Also geography of Uttarakhand (for state paper) if applicable.
What you should do:
-
After downloading the official notification for the subject you are applying for, check the “Concerned Subject” syllabus section for that subject.
-
Use your post-graduate subject textbooks and standard references because the questions will test teaching level understanding.
4. Preparation Strategy
-
Download the official PDF of the syllabus & exam pattern from UKPSC website to ensure you have the latest version.
-
Cover the core/general sections (Hindi, English, Teaching Aptitude/Reasoning, General Awareness) first since they apply to all aspirants.
-
Then focus on the discipline subject thoroughly: revision of PG level topics, understanding of fundamentals, previous year questions.
-
Work on time management and mock tests (especially for the objective MCQ pattern). Prior year papers are available.
-
Since there is negative marking in some cases, accuracy is important.
Best Book for UKPSC Lecturer Exam
The best books and study materials you can use to prepare effectively for the UKPSC Lecturer Exam (Uttarakhand Public Service Commission Lecturer Cadre), especially for the Screening Test (Paper-I) and Subject Papers (Paper-II):
Top Recommended Books for UKPSC Lecturer Exam
1. General UKPSC Lecturer Practice and Solved Papers
-
Uttarakhand Lecturer Cadre Exam Practice Sets (General) – Practice sets with solved papers for both Paper-I & Paper-II tailored to UKPSC’s current pattern. Covers GK, reasoning, general studies & more with revision notes.
2. Subject-Specific UKPSC Lecturer Guides (Per Discipline)
These are useful if you’re preparing for a specific subject (e.g. Civics, Hindi, English, Geography, Maths):
-
Uttarakhand Lecturer Civics Practice Sets & Solved Papers (Arihant) – Includes 14 practice sets + previous year papers + quick revision notes.
-
Uttarakhand Lecturer Hindi / English Study Guides (Arihant) – Exam-pattern based practice and explanations for different mediums.
-
Uttarakhand Lecturer Geography / Maths Guides (Arihant) – Focused practice for specific subjects with PYQs and topics structured per syllabus.
3. Subject Books by Discipline (Other Publishers)
If you want more in-depth grounding in your optional/subject:
-
UKPSC Lecturer Physics Preparation Book (2026 Edition) – Covers syllabus and solved questions for Physics.
-
UKPSC Lecturer Biology Preparation Book (2025 Edition) – Comprehensive syllabus + practice for Biology learners.
-
UKPSC Lecturer Arts / General Preparation Books – Often include solved questions and exam tips for Arts stream.
4. State-Specific GK & Current Affairs
Since the UKPSC exam includes a significant Uttarakhand GK section, consider adding:
-
Uttarakhand History & District Notes – Helps cover regional history & culture.
-
Current Affairs compilations focused on Uttarakhand – Useful for recent events and updates relevant to the exam.
FAQs
1. What is the selection process for the UKPSC Lecturer exam?
-
For the Lecturer (Pravakta/Group-C) posts, the selection process typically includes a Screening Test and a Subject Knowledge (Mains) Test.
-
For the Polytechnic Lecturer posts, there are three papers (General Hindi, General English for certain subjects, and the Concerned Subject) followed by an interview. Syllabus4U
2. How is the exam pattern structured?
-
For the Screening Test: objective type, e.g., 150 marks, duration ~2 hours.
-
For the Subject Knowledge Test: objective questions on the subject opted by the candidate, higher marks and longer duration.
-
Example for Polytechnic Lecturer:
-
Paper I: General Hindi — 100 questions, 100 marks, 2 hours.
-
Paper II: General English (for specified subjects) — 100 questions, 100 marks, 2 hours.
-
Paper III: Concerned Subject — 150 questions, 300 marks, 3 hours.
-
3. Is there negative marking in the UKPSC Lecturer exam?
Yes — for some papers there is.
For example: for the Polytechnic Lecturer exam, there is a negative marking of ¼ mark for each wrong answer.
4. What topics are included in the syllabus for Lecturer posts?
-
For the Screening Test/General Test: includes Teaching Aptitude, General Awareness/Aptitude, and basic subjects.
-
For the Subject Knowledge Test: the entire subject opted (such as Mathematics, Chemistry, Biology etc) is covered.
-
For example: In the Mathematics syllabus you’ll find topics like Sets, Relations, Mappings, Groups, Matrices, Differential Calculus.
5. Do I have to cover the entire syllabus, or only the “important” parts?
You must cover the entire syllabus. Questions can come from any part of the syllabus. (Testbook article for Lecturer says: “You must cover the entire syllabus as questions can be asked from any topic…”).
6. How many marks does each question carry?
According to available pattern information: yes, each question carries 1 mark in objective portions.
7. What is the eligibility for the Lecturer posts?
-
Candidates typically require a Post-Graduate degree in the relevant subject and a B.Ed or LT Diploma (as applicable) for Lecturer posts in Uttarakhand.
-
Age limits, service residency etc apply as per official notification.
8. Where can I get previous year papers and practice material?
You can download previous year papers for the UKPSC Lecturer exam from various educational websites. They help in understanding the pattern and difficulty level.
9. Is the syllabus/structure for 2026 different from earlier years?
Yes – there are updates and changes. For example, the exam pattern for the Polytechnic Lecturer shows three papers in 2026.
It’s important to refer to the latest official notification for the year you are applying for.
10. What’s the recommended strategy to prepare based on this syllabus?
-
Thoroughly map out each topic in the syllabus and allocate study time accordingly.
-
Practice subject-wise question banks (especially for your subject knowledge test).
-
Solve previous years’ papers to get comfortable with pattern and time management.
-
For objective papers, practice MCQs with negative marking in mind.
-
Stay updated with the official notification for any changes.