CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2025-26 in Details
The CBSE Class 10 Mathematics syllabus for the academic year 2025-26 includes a comprehensive range of topics divided into seven units. Here’s a detailed overview:
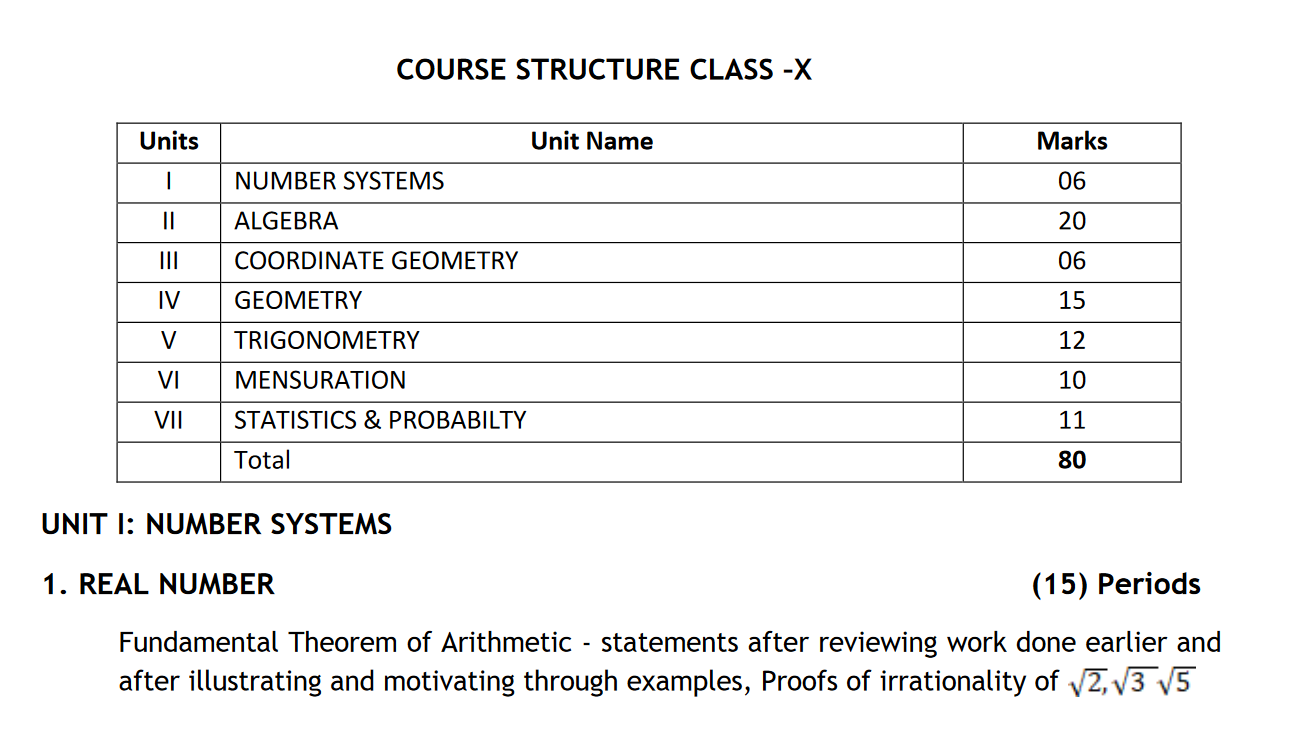
UNIT I: NUMBER SYSTEMS
1. REAL NUMBER (15) Periods
Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic – statements after reviewing work done earlier andafter illustrating and motivating through examples, Proofs of irrationality of root 2, 3, 5.
UNIT II: ALGEBRA
1. POLYNOMIALS (8) Periods
Zeros of a polynomial. Relationship between zeros and coefficients of quadratic
polynomials.
2. PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES (15) Periods
Pair of linear equations in two variables and graphical method of their solution, consistency/inconsistency. Algebraic conditions for number of solutions. Solution of a pair of linear equations in two variables algebraically – by substitution, by elimination. Simple situational problems.
3. QUADRATIC EQUATIONS (15) Periods
Standard form of a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, (a ≠ 0). Solutions of quadratic equations (only real roots) by factorization, and by using quadratic formula. Relationship between discriminant and nature of roots. Situational problems based on quadratic equations related to day to day activities to be incorporated.7
4. ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS (10) Periods
Motivation for studying Arithmetic Progression Derivation of the nth term and sum of the first n terms of A.P. and their application in solving daily life problems.
UNIT III: COORDINATE GEOMETRY
Coordinate Geometry (15) Periods
Review: Concepts of coordinate geometry, graphs of linear equations. Distance formula. Section formula (internal division).
UNIT IV: GEOMETRY
1. TRIANGLES (15) Periods
Definitions, examples, counter examples of similar triangles.
1. (Prove) If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two
sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
2. (Motivate) If a line divides two sides of a triangle in the same ratio, the line is parallel
to the third side.
3. (Motivate) If in two triangles, the corresponding angles are equal, their corresponding
sides are proportional and the triangles are similar.
4. (Motivate) If the corresponding sides of two triangles are proportional, their
corresponding angles are equal and the two triangles are similar.
5. (Motivate) If one angle of a triangle is equal to one angle of another triangle and the
sides including these angles are proportional, the two triangles are similar.
2. CIRCLES (10) Periods
Tangent to a circle at, point of contact
1. (Prove) The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the
point of contact.
2. (Prove) The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.8
UNIT V: TRIGONOMETRY
1. INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY (10) Periods
Trigonometric ratios of an acute angle of a right-angled triangle. Proof of their
existence (well defined); motivate the ratios whichever are defined at 0o and 90o. Values
of the trigonometric ratios of 300, 450 and 600. Relationships between the ratios.
2. TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (15) Periods
Proof and applications of the identity sin2A + cos2A = 1. Only simple identities to be
given.
3. HEIGHTS AND DISTANCES: Angle of elevation, Angle of Depression. (10)Periods
Simple problems on heights and distances. Problems should not involve more than two
right triangles. Angles of elevation / depression should be only 30°, 45°, and 60°.
UNIT VI: MENSURATION
1. AREAS RELATED TO CIRCLES (12) Periods
Area of sectors and segments of a circle. Problems based on areas and perimeter /
circumference of the above said plane figures. (In calculating area of segment of a
circle, problems should be restricted to central angle of 60°, 90° and 120° only.
2. SURFACE AREAS AND VOLUMES (12) Periods
Surface areas and volumes of combinations of any two of the following: cubes, cuboids,
spheres, hemispheres and right circular cylinders/cones.
UNIT VII: STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY
1. STATISTICS (18) Periods
Mean, median and mode of grouped data (bimodal situation to be avoided).
2. PROBABILITY (10) Periods
Classical definition of probability. Simple problems on finding the probability of an
event.
Question Paper Design
The exam structure includes different types of questions aimed at assessing various skills, including remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. The distribution is approximately:
- Remembering: 43 Marks (54%)
- Understanding: 19 Marks (24%)
- Applying and Analyzing: 18 Marks (22%)
Important Topics
Key focus areas include:
- Prime factorization and proofs of irrationality in Real Numbers.
- Relationship between zeros and coefficients in Polynomials.
- Graphical methods for solving Linear Equations.
- Properties of triangles and circles in Geometry
1. Mathematics – Textbook for class IX – NCERT Publication
2. Mathematics – Textbook for class X – NCERT Publication
3. Guidelines for Mathematics Laboratory in Schools, class IX – CBSE Publication
4. Guidelines for Mathematics Laboratory in Schools, class X – CBSE Publication
5. Laboratory Manual – Mathematics, secondary stage – NCERT Publication
6. Mathematics exemplar problems for class IX, NCERT publication.
7. Mathematics exemplar problems for class X, NCERT publication.
CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2025-26 PDF Download
You can download the CBSE Class 10 Maths syllabus for the 2025-26 academic year by visiting the official website of the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). Here’s how you can access it:
- Visit the official CBSE website: cbse.gov.in
- Navigate to the “Curriculum” section: Look for the “Curriculum 2025-26” tab on the homepage.
- Select the “Secondary Curriculum” option: Under this, choose Class 10.
- Download the Maths Syllabus: Find the Maths subject and click on the link to download the syllabus in PDF format.
Alternatively, I can guide you to trusted educational sites that offer direct PDF download links for the CBSE syllabus that is Syllabus4u. Click on the below to get the PDF.
How to prepare CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2026?
To prepare for the CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus effectively and in a timely manner, here’s a comprehensive strategy:
Understand the Syllabus Thoroughly
- Get a Copy of the Syllabus: Start by downloading or obtaining a printed copy of the official CBSE Class 10 Maths syllabus.
- Know the Topics: The syllabus includes topics like Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry, Statistics, Probability, and more. Knowing each section’s weightage and difficulty level helps prioritize.
Create a Study Plan
- Divide the Syllabus: Break down the syllabus into manageable chunks for each month. Aim for covering specific chapters each week.
- Set Realistic Goals: Define specific goals for each day or week (e.g., completing one chapter or practicing a set number of problems).
- Prioritize Difficult Topics: Focus more on topics that you find difficult or that carry more marks.
Use NCERT Textbooks and Reference Books
- NCERT First: Ensure you are well-versed with your NCERT textbook as it is the primary source for Class 10 Maths.
- Reference Books: If needed, refer to additional books like RD Sharma, RS Aggarwal, or ML Aggarwal for extra practice.
Conceptual Understanding Over Rote Learning
- Master the Concepts: Maths requires understanding the core concepts and formulas rather than memorization. Make sure you understand the reasoning behind each concept.
- Interactive Learning: Use online resources or videos to understand complex topics better.
Practice Regularly
- Solve Examples: Practice solving every example given in the NCERT textbook.
- Solve Previous Year Papers: Go through previous year’s CBSE exam papers to understand the pattern and frequently asked questions.
- Sample Papers: Regularly solve sample papers to improve your speed and accuracy.
- Time Yourself: Practice under exam-like conditions to get used to the time constraints.
Work on Weak Areas
- Focus on Mistakes: After solving practice papers, analyze mistakes and work on weak areas.
- Get Help: Don’t hesitate to ask teachers, peers, or online platforms if you’re struggling with any topic.
Revise Periodically
- Regular Revision: Set aside time for revision at regular intervals (e.g., every 2-3 weeks). Go over the chapters you’ve completed to retain information.
- Create Short Notes: Write concise notes with key formulas and concepts to quickly refer to during revision.
Time Management
- Avoid Last-Minute Cramming: Ensure that you begin your preparation well in advance and avoid rushing at the last moment.
- Balanced Schedule: While studying Maths, don’t neglect other subjects. A balanced approach ensures you don’t burn out and are able to retain information for longer periods.
Stay Consistent and Positive
- Stay Motivated: Maintain a positive mindset throughout your preparation. Consistency and patience are key to mastering Maths.
- Take Breaks: Avoid long, uninterrupted study sessions. Taking short breaks can help refresh your mind.
Use Online Tools for Extra Practice
- Online Practice Platforms: Websites like Adda247 offer free resources and practice exercises that can enhance your preparation.
By maintaining a steady pace, practicing regularly, and reviewing important topics periodically, you can ensure timely and effective preparation for the CBSE Class 10 Maths exam.
Books to Cover Class 10 Maths Syllabus
list of books to cover the CBSE Class 10 Maths syllabus effectively — including core textbooks, practice books, and revision guides that many toppers and teachers suggest:
1. NCERT Mathematics Textbook (Class 10) (Must-have)
-
Publisher: NCERT
-
Why it’s essential: This is the official CBSE textbook and covers the entire syllabus chapter-wise with examples, exercises and clear explanations. CBSE board questions are directly based on NCERT content and exercise questions.
Make sure to do all solved examples and exercises thoroughly.
2. NCERT Exemplar Problems (Class 10 Maths)
-
Publisher: NCERT
-
Why use it: Contains higher-order thinking questions, challenging problems and application-based questions that help strengthen concepts and improve problem-solving skills.
3. R.D. Sharma – Mathematics for Class 10
-
Why it’s good:
-
Extremely comprehensive with a huge variety of problems (basic to advanced)
-
Helps build conceptual depth and exam readiness
-
Widely recommended for board exam prep and competitive practice.
-
4. R.S. Aggarwal – Secondary School Mathematics for Class 10
-
Why use it:
-
Good for step-by-step practice questions
-
Helps reinforce basic techniques and improves speed
-
Suitable if you want more variety in topic practice.
-
5. Arihant – All in One Mathematics CBSE Class 10
-
Why it’s useful:
-
Combines theory, examples, practice, and sample papers
-
Includes previous years’ board questions and solutions
-
Great for complete syllabus practice and revision.
-
6. Chapter-wise Question Banks & Sample Papers (for revision)
Useful books to practice exam-style questions and improve time management closer to board exams:
-
Oswaal CBSE Sample Question Papers Class 10 Maths
-
Educart CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Papers
-
MTG / Disha / U-Like Sample Papers
These books often include previous year questions (PYQs), model papers, and board-pattern tests which are extremely helpful for last-minute revision and scoring trends.
Study Strategy Tips
Start with NCERT textbook + Exemplar, complete every exercise and solved example.
Use RD Sharma (or RS Aggarwal) for deeper practice and difficult questions.
In the last few months before exams, focus on question banks and sample papers to get used to board-style questions and timing.
Some students also find revising with chapter-wise short notes and formula sheets useful.
Quick Summary (Best Combo)
| Purpose | Recommended Books |
|---|---|
| Core syllabus & concepts | NCERT Textbook |
| Difficult/problem-solving questions | NCERT Exemplar, RD Sharma |
| Extra practice | RS Aggarwal, Arihant All in One |
| Revision & board pattern practice | Oswaal/Educart Sample Papers & Question Banks |
FAQs
1. What are the main topics covered in the CBSE Class 10 Maths syllabus?
The main topics include:
- Number Systems
- Algebra (Polynomials, Linear Equations)
- Geometry (Triangles, Circles, Constructions)
- Trigonometry (Heights and Distances)
- Coordinate Geometry
- Statistics and Probability
- Surface Areas and Volumes
- Arithmetic Progressions
2. Is the CBSE Class 10 Maths syllabus the same for all students?
Yes, the syllabus is the same for all students, but students can choose between Basic and Standard levels for the Maths exam. The content is similar, but the level of difficulty differs.
3. How many chapters are included in the CBSE Class 10 Maths syllabus?
The syllabus typically includes 15 chapters. These are divided across various topics like algebra, geometry, statistics, and arithmetic, which build the foundation for higher studies.
4. What is the weightage of different topics in the CBSE Class 10 Maths exam?
The weightage varies each year, but generally:
- Algebra (Polynomials, Linear Equations) and Geometry (Triangles, Circles) hold significant weight.
- Trigonometry and Coordinate Geometry also carry a moderate weight.
- Surface Area and Volumes and Statistics are usually lighter but important.
5. What is the difference between the Basic and Standard Maths exams?
- The Basic Maths exam is designed for students who find mathematics challenging. The questions are of a lower difficulty level.
- The Standard Maths exam is for students who wish to pursue mathematics in higher studies. It covers the same syllabus as Basic but with more advanced and complex questions.
Related Post:

1 thought on “CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2025-26, PDF Download”