The ISC Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26 provides a structured approach to mastering key concepts in physical, inorganic, and organic chemistry. It includes detailed study areas like solutions, electrochemistry, chemical kinetics, coordination compounds, and biomolecules, ensuring students gain a comprehensive understanding of both theoretical and practical aspects. The syllabus is designed to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills through a mix of numericals, chemical reactions, and experimental work. With a balanced focus on theory and hands-on experiments, this curriculum prepares students for both board exams and higher studies in science-related fields.
ISC Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26
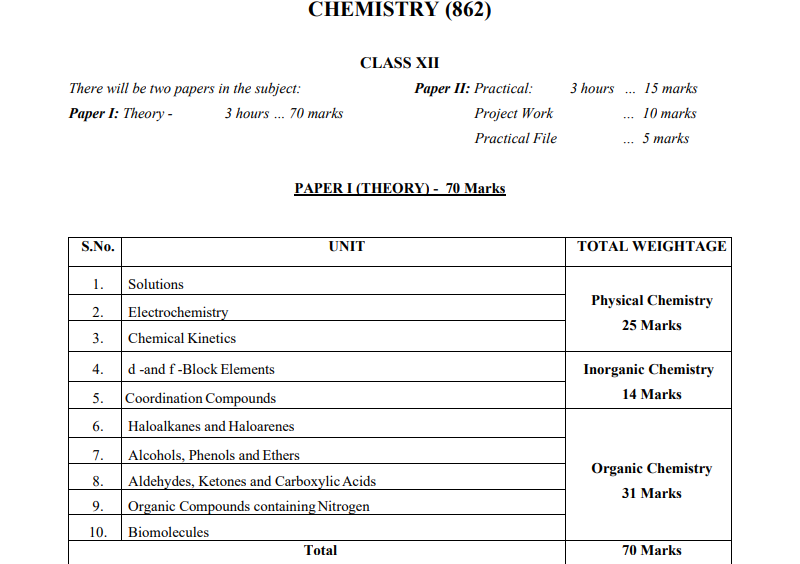
This document outlines the ISC Chemistry syllabus for Class 12 for the academic year 2025-2026. It provides a comprehensive breakdown of the theory, practical, and project work sections. Paper I (Theory) will be 70 marks, Paper II (Practical) will be 15 marks, and Project Work will contribute 10 marks. The syllabus is divided into three main branches: Physical Chemistry, Inorganic Chemistry, and Organic Chemistry, covering key topics in each area.
Paper I: Theory – 70 Marks
The theory paper is divided into 10 units with a detailed breakdown of each topic, including definitions, explanations, and numericals. Below is a summary of the units and their weightage:
| S.No. | Unit | Weightage (Marks) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Solutions (Physical Chemistry) | 25 |
| 2 | Electrochemistry (Physical Chemistry) | |
| 3 | Chemical Kinetics (Physical Chemistry) | |
| 4 | d and f Block Elements (Inorganic Chemistry) | 14 |
| 5 | Coordination Compounds (Inorganic Chemistry) | |
| 6 | Haloalkanes and Haloarenes (Organic Chemistry) | 31 |
| 7 | Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers (Organic Chemistry) | |
| 8 | Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids (Organic Chemistry) | |
| 9 | Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen | |
| 10 | Biomolecules |
Detailed Topics:
- Solutions:
- Types of solutions: solid in liquid, liquid in liquid, gases in liquids, and solid solutions.
- Colligative properties (Raoult’s Law, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, osmotic pressure).
- Use of colligative properties to determine molecular mass.
- van’t Hoff factor for dissociation/association in solutions.
- Numerical problems based on concentration measures like molarity, molality, and mole fraction.
- Electrochemistry:
- Types of cells: electrolytic and electrochemical.
- Key concepts: EMF of cells, Nernst equation, electrode potential, Faraday’s laws of electrolysis.
- Batteries: Dry cell, lead storage battery, fuel cells.
- Corrosion and its prevention.
- Chemical Kinetics:
- Rate of reactions, factors affecting reaction rate.
- Concepts of order and molecularity.
- Half-life calculations for zero and first-order reactions.
- Arrhenius equation and the effect of temperature on reaction rates.
- d- and f-Block Elements:
- Properties of transition metals (ionization energy, oxidation states, catalytic properties).
- Lanthanoids and Actinoids: Properties and uses.
- Preparation and properties of potassium permanganate and potassium dichromate.
- Coordination Compounds:
- Ligands, coordination number, and oxidation states.
- IUPAC nomenclature, isomerism (structural and stereo).
- Werner’s theory, valence bond theory (VBT), and crystal field theory (CFT).
- Importance in qualitative analysis and metal extraction.
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes:
- Preparation methods, properties, and reactions.
- Substitution reactions (SN1 and SN2 mechanisms).
- Environmental effects of compounds like DDT and freons.
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers:
- Classification and properties of alcohols and phenols.
- Dehydration mechanisms and oxidation reactions.
- Williamson synthesis for ether preparation.
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids:
- Methods of preparation, nucleophilic addition reactions.
- Oxidation, reduction, and condensation reactions.
- Uses of aldehydes and ketones.
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen:
- Amines: Classification, preparation, and basic nature.
- Diazonium salts: Preparation and applications in organic synthesis.
- Biomolecules:
- Carbohydrates: Structure of glucose, fructose, starch, and cellulose.
- Proteins: Amino acids, peptide bonds, and structure of proteins.
- Vitamins and nucleic acids (DNA, RNA).
Paper II: Practical Work – 15 Marks
Experiments include:
- Titrations:
- Redox titrations using potassium permanganate.
- Calculation of molarity and molecular mass.
- Rate of Reaction Studies:
- Reactions like sodium thiosulphate and hydrochloric acid with graphs.
- Identification of Organic Compounds:
- Tests for functional groups like alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids.
- Electrochemistry:
- Setting up voltaic cells and measuring potential.
- Qualitative Analysis:
- Identification of salts using systematic analysis for one anion and one cation.
ISC Class 12 Chemistry Practical Syllabus 2026
The ISC Class 12 Chemistry Practical syllabus is divided into two parts: Practical Work and Project Work & Viva Voce. Below is the detailed syllabus based on the ISC guidelines:
1. Practical Work
A. Quantitative Analysis (Volumetric Analysis)
- Titrations
- Oxidation-reduction titrations (e.g., KMnO₄ with Fe²⁺, oxalic acid).
- Acid-base titrations (e.g., NaOH with HCl).
- Iodometry (e.g., thiosulphate with iodine).
B. Qualitative Analysis (Salt Analysis)
- Identification of Cations
- Cations to be analyzed: NH4+,Pb2+,Cu2+,Al3+,Fe3+,Zn2+,Ca2+,Ba2+,Sr2+,Mg2+.
- Identification of Anions
- Anions to be analyzed: CO32−,SO32−,Cl−,Br−,NO3−,SO42−,CH3COO-.
C. Preparation of Inorganic Compounds
Examples include:
- Preparation of Mohr’s salt\text{Mohr’s salt} (Ferrous ammonium sulfate).
- Preparation of Potash alum\text{Potash alum} (Double sulfate of potassium and aluminum).
D. Experiments Related to pH
- Study the change of pH of solutions by adding strong acids and bases.
- Identify the pH using pH papers or universal indicator.
E. Chemical Kinetics
- Study of reaction rates (e.g., reaction between sodium thiosulphate and HCl).
F. Electrochemistry
- Determination of EMF of a cell.
2. Project Work & Viva Voce
- Students must complete a chemistry-related project. The project can be an investigation, model, or theoretical work. Some examples include:
- Analysis of soft drinks for acidic content.
- Estimation of Vitamin C in fruit juices.
- Comparative study of different soaps/detergents.
- Viva Voce will be based on the project and practicals performed during the year.
3. Evaluation Scheme
| Component | Marks |
|---|---|
| Practical Work | 20 |
| Project Work | 10 |
| Viva Voce | 10 |
| Total | 40 |
Project Work and Practical File – 15 Marks
- Project Work: Students will carry out creative chemistry projects, with a few suggested topics like amino acids, vitamins, and nucleic acids.
- Practical File: The chemistry practical file will be evaluated based on completeness and accuracy of recorded experiments.
ISC Class 12 Chemistry Exam Pattern 2026
ISC Class 12 Chemistry Exam Pattern for the 2026 board examinations (Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations -CISCE). This pattern helps you understand how marks are distributed, paper structure, and components of assessment so you can plan your study strategy effectively.
ISC Class 12 Chemistry Exam Pattern 2026
Total Marks & Components
| Component | Marks | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Theory Paper (Paper I) | 70 | Written exam testing conceptual understanding and application. |
| Practical & Internal Assessment (Paper II) | 30 | Consists of practical experiments, project work and practical file. |
| Total | 100 | Final score for the subject. |
Theory Paper (70 Marks)
The theory paper typically includes a mix of objective and descriptive questions covering Physical, Inorganic, and Organic Chemistry.
Paper Structure
-
Multiple Choice / Objective Questions
-
Short Answer Questions
-
Long Answer / Descriptive Questions
-
Numerical & Application-Based Problems
Questions are set to test conceptual clarity, numerical skills, and application of topics.
Note: The exact section names/number of questions may vary slightly based on the official specimen paper from CISCE, but total theory marks remain 70.
Practical & Internal Assessment (30 Marks)
The practical component assesses your hands-on skills in the laboratory and includes:
| Practical Component | Marks |
|---|---|
| Practical Examination | 15 |
| Project Work | 10 |
| Practical File / Record | 5 |
The practical exam typically includes experiments, qualitative analysis, viva voce, and correct recording of observations.
Suggested Unit-Wise Weightage (Indicative)
While the official board doesn’t release exact unit marks early, many preparatory guides suggest focusing on these broad divisions in the theory paper:
| Unit Area | Approx. Marks (Indicative) |
|---|---|
| Physical Chemistry | ~25 |
| Inorganic Chemistry | ~14 |
| Organic Chemistry | ~31 |
This helps in prioritising revision across important topics.
Unit distribution and exact questions may vary each year, but the total theory remains 70 marks and practical 30 marks.
Exam Duration & Mode
-
Theory Paper Duration: Typically 3 hours (may be specified by CISCE timetable).
-
Mode: Offline (Pen & Paper).
ISC Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26 PDF Download
The ISC Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus can be downloaded in PDF format for the academic year 2025-26. This PDF provides all the necessary details for theory, practicals, and project work, making it easier for students to prepare.
ISC Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus -Click Here To Download PDF
FAQs Based on ISC Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus
1. What is the syllabus of ISC Class 12 Chemistry?
The ISC Class 12 Chemistry syllabus is divided into Physical Chemistry, Organic Chemistry, and Inorganic Chemistry, along with practical work. Major units include Electrochemistry, Chemical Kinetics, Coordination Compounds, Haloalkanes & Haloarenes, Alcohols, Aldehydes & Ketones, Amines, Biomolecules, and Chemistry in Everyday Life.
2. How many units are there in ISC Class 12 Chemistry?
There are 16 theory units prescribed by CISCE, covering core concepts of chemistry and their real-life applications. Practical chemistry is assessed separately.
3. Which section carries the highest weightage in the ISC Chemistry exam?
Organic Chemistry generally carries the highest weightage in the ISC Class 12 Chemistry examination, followed by PhysicalChemistry. Students should focus on reaction mechanisms and named reactions.
4. Is the ISC Class 12 Chemistry syllabus difficult?
The syllabus is considered concept-based and application-oriented. While it is slightly more detailed than some boards, regular practice and clarity of concepts make it manageable.
5. Are numerical problems important in ISC Chemistry?
Yes, numerical problems are very important, especially from chapters like Electrochemistry, Chemical Kinetics, and Solutions. They frequently appear in both short and long answer questions.
6. How important are practicals in ISC Class 12 Chemistry?
Practicals carry 30 marks and are crucial for scoring well. They include qualitative analysis, titration, project work, and viva voce.
7. Which chapters are most important for board exams?
High-scoring and frequently asked chapters include:
-
Electrochemistry
-
Coordination Compounds
-
Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers
-
Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids
-
Amines
-
Biomolecules
8. Does ISC Chemistry syllabus help in competitive exams like JEE or NEET?
Yes, the ISC syllabus builds strong conceptual foundations that are helpful for competitive exams, though some additional topics may need to be covered separately.
9. Are reaction mechanisms required in detail?
Yes, reaction mechanisms, conditions, catalysts, and named reactions are very important and often asked in descriptive questions.
10. What is the best way to prepare for ISC Class 12 Chemistry?
-
Understand NCERT + ISC-prescribed textbooks
-
Practice numerical problems daily
-
Revise organic reactions regularly
-
Focus on diagrams and chemical equations
-
Practice previous years’ question papers
11. Are diagrams and structures important in the exam?
Yes, neat chemical structures, diagrams, and balanced equations fetch full marks and improve answer presentation.
12. Is Chemistry in Everyday Life important for exams?
Yes, it is a theory-based, scoring chapter and is often used for short-answer or conceptual questions.
13. Are internal choices provided in the exam?
Yes, the ISC Chemistry paper usually includes internal choices, allowing students flexibility in attempting questions.
14. How many marks is the ISC Chemistry theory exam?
The theory paper is of 70 marks, and the remaining 30 marks are for practical assessment.
15. Where can students get the official ISC Class 12 Chemistry syllabus?
Students can download the official syllabus from the CISCE (Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations) website or refer to their school’s academic guidelines.
Related Post:
| ISC Class 12 Legal Studies Syllabus | ISC Class 12 Biology Syllabus |
| ISC Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus | ISC Class 12 Physics Syllabus |
| ISC Class 12 Maths Syllabus | ISC Class 12 English Syllabus |